AWS DataSync
Overview
There are frequently situations where moving data between various environments is necessary. The effort needed to transfer data using a unique technical solution could differ depending on the volume of data to be moved between different locations and services, AWS introduced AWS Data Sync, an AWS-managed data movement service, to provide a seamless data transfer and discovery service. This service aids in data migration and the quick acceleration of workloads between various environments. A DataSync task can use a 10Gbps network and send 10 Gb of data per second, making it suitable for large data transfers.
What is AWS DataSync?
AWS DataSync is a data migration and discovery service that enables reliable and secure large-scale data migration to the desired location. By automating the transfer process and supporting bandwidth throttling and transfer scheduling as needed, AWS DataSync makes it easier to transfer data between various storage systems and services. Network File System (NFS) file servers, Server Message Block (SMB) file servers, Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Object storage systems, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets, Amazon EFS, Amazon FSx, and AWS Snowcone Devices are the storage systems that are supported by AWS DataSync for data transfer.
For instance, if a business needs to archive its petabytes of on-premises data to the archival storage class of AWS Simple Storage Service, it can use AWS DataSync to quickly and easily move its on-premises data to the AWS cloud.
Features of AWS DataSync
The following list highlights a few of the many common features:
- Data Migration: AWS DataSync supports a number of storage services from which data can be copied back and forth. The storage systems that are supported by AWS DataSync for data transfer include Network File System (NFS) file servers, Server Message Block (SMB) file servers, Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Object storage systems, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets, Amazon EFS, Amazon FSx, and AWS Snowcone Devices.
- Bandwidth Control: AWS DataSync also allows you to control the amount of bandwidth used in data transfers. DataSync supports network links up to 10Gbps and allows you to set a bandwidth cap so that AWS DataSync doesn't use the entire network link.
- Data Transfer Scheduling: Additionally, AWS DataSync supports the automatic scheduling of data transfers at predetermined intervals, eliminating the need for future data transfers to be manually initiated.
- Data Encryption: Data migration and storage can be done securely and reliably with the help of AWS DataSync, which supports data encryption both in transit and at rest.
How AWS DataSync Works
AWS DataSync Terminology:
It's crucial to comprehend the terminology used in AWS Data Sync before understanding its workings and architecture.
- Agent: An agent is used to read and write data from storage systems. As part of the initial setup, an agent must be installed on a virtual machine. It can be set up on an Amazon EC2 instance, a Microsoft Hypervisor, a Linux Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), or VMware ESXi. AWS offers images with agents set up for various virtual machine setups that can be downloaded from the AWS DataSync console.
- Location: For data transfer, location specifies the source and destination locations.
- Task: The specifics of data transfer, such as location, data transfer mechanism, metadata, and permissions, are defined by a task.
- Task execution: A task that is being executed is in the DataSync task execution phase.
AWS DataSync Transfer Architecture:
Let's consider an industry that wants to move its on-premise data to AWS S3 as an example to better understand how AWS DataSync transfer functions. A successful DataSync transfer will require the setting up of the following steps.
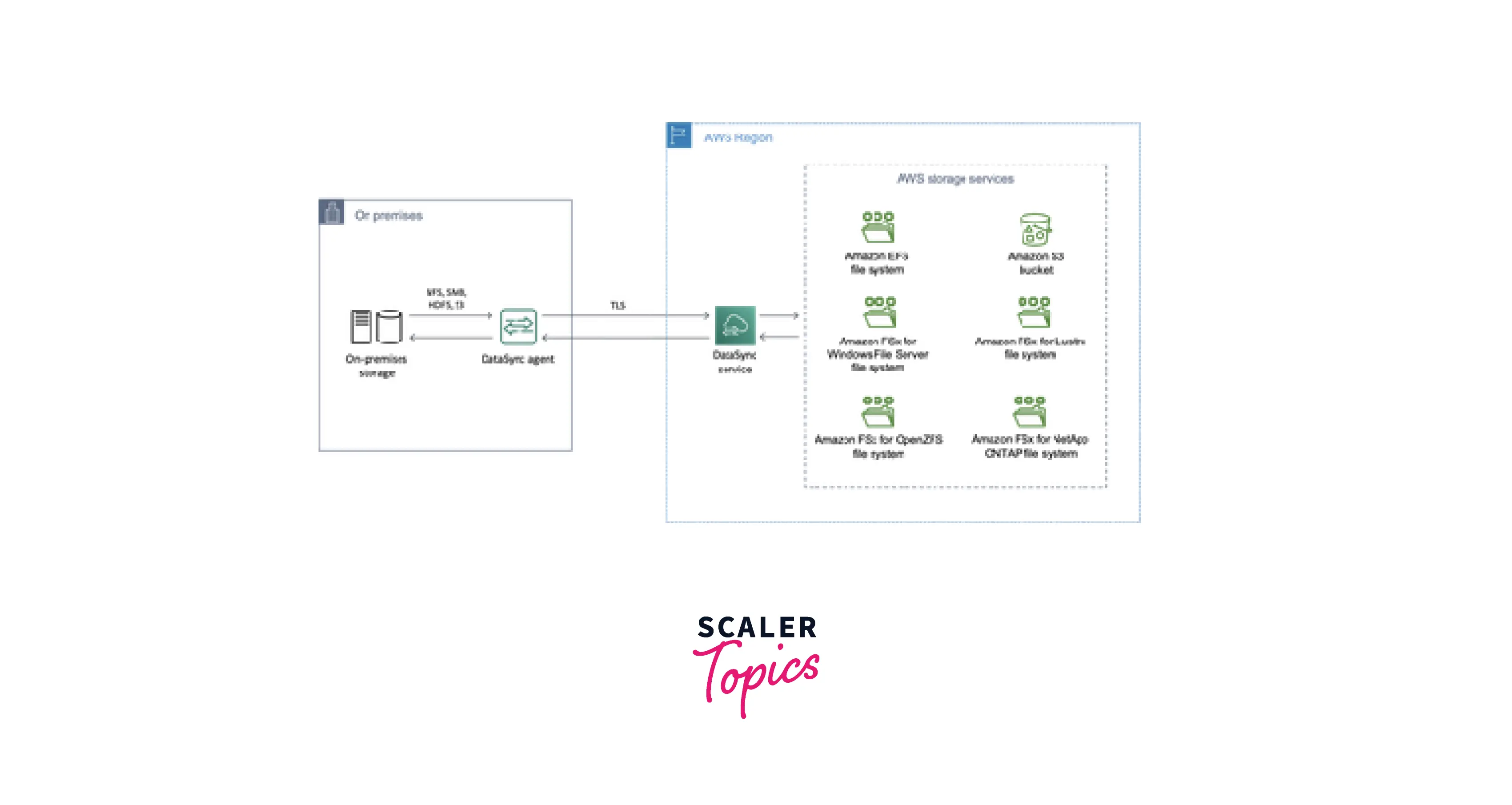
- Create an Agent: From the on-premises network, download and install the DataSync agent on the preferred virtual machine platform. The AWS console allows you to download an image for the selected VM platform with a ready-to-use agent installation.
- Specify Service Endpoint: The endpoint that DataSync uses to communicate with AWS must be specified; it may be a public service endpoint, a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) endpoint, or a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) endpoint.
- Activate the agent: The DataSync agent should now be activated using the AWS DataSync console.
- Configure Source and Destination Location: The chosen data transfer should have a source and destination location created. In our example, set up a Network File System (NFS) as the source location for an on-premises source location and an S3 bucket as the destination location.
- Configure and Review Task: Review and create the task after configuring it with additional features like bandwidth control, data scheduling, etc.
- Start the task: Start the task next to advance it to the execution phase.
Data will be transferred from an on-premises source location to an AWS S3 location as a result of the aforementioned process.
Use Cases of AWS DataSync
- Migrate data to Cloud: One of the most popular use cases is the quick transfer of data using AWS DataSync from any on-premises source location to the AWS cloud.
- Data Backup: AWS DataSync can be used to automatically back up data to the AWS cloud to a preferred storage location. High availability is ensured by data replication across multiple availability zones.
- Data Archival: When data needs to be archived to an AWS cloud storage location like S3 Glacier, DataSync can also be taken into consideration as a transfer option.
- Data Processing: DataSync can move data to the cloud and back to the source location for processing data using other AWS services, making it simple to analyze the results later.
Benefits of AWS DataSync
- Automate data transfer – After setup, AWS DataSync enables automation of data transfer between various storage services with little to no manual intervention needed.
- Data encryption – Data transfer and storage over a network are made secure by AWS DataSync, which provides data encryption both in transit and at rest.
- Multi-cloud support – AWS DataSync makes cross-cloud transfer quick and simple by enabling data transfer from other cloud service providers as well.
- Reduce costs – The cost of using AWS DataSync is based on the amount of data transferred; per-gigabyte pricing reduces the overall cost of data transfer when compared to other conventional methods of data transfer.
AWS DataSync Pricing
Pay-as-you-go billing is the standard for AWS DataSync. The amount of data migrated determines the per-gigabyte fee. Each AWS Region has different pricing. The use of other AWS services, such as S3, EFS, Fsx, etc., is additionally charged in accordance with their rates.
AWS DataSync vs Storage Gateway
An on-premises customer can access virtually unlimited cloud storage through the hybrid cloud storage service known as AWS Storage Gateway. Customers can use AWS storage with Storage Gateway's standard set of storage protocols, including iSCSI, SMB, and NFS, without having to change the way their current applications work. By enabling data to be sent directly to the AWS cloud, the storage gateway is a way to extend the on-premise storage.
- Storage Gateway is a virtual extension that enables the use of cloud storage, whereas AWS DataSync is a service that allows data to be moved to various AWS storage solutions.
- While Storage Gateway only supports S3 and FSx for Windows File Server cloud storage, AWS DataSync can work with multiple AWS storage services like EFS, Fsx, and S3.
- While Storage Gateway supports NFS, SMB, and iSCSI protocols, AWS DataSync uses an AWS-designed transfer protocol.
- While Storage Gateway charges according to the type and amount of storage used, the requests made, and the amount of data transferred outside of AWS, AWS DataSync pricing is flat-rate based on the amount of data being transferred.
Conclusion
- AWS DataSync is a data migration and discovery service that enables reliable and secure large-scale data migration. It automates the transfer process and supports bandwidth throttling and transfer scheduling as needed. Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets, Amazon EFS, and AWS Snowcone Devices are supported.
- Features of DataSync include data migration, data encryption, bandwidth control, and task scheduling.
- An agent is used to read and write data from storage systems. It can be set up on an Amazon EC2 instance, a Microsoft Hypervisor, or a Linux Kernel-based Virtual Machine. The specifics of data transfer, such as location, metadata, and permissions, are defined by a task.
- Transferring data quickly from any on-premises source location to the AWS cloud using AWS DataSync is one of the most common use cases. It is also used for data backups, data archival, and data processing.
- The amount of data migrated determines the per-gigabyte fee. Pay-as-you-go billing is the standard for AWS DataSync. The use of other AWS services, such as S3, EFS, Fsx, etc., is additionally charged in accordance with their rates.
- AWS DataSync is a service that allows data to be moved to various AWS storage solutions. While Storage Gateway only supports S3 and FSx for Windows File Server cloud storage, AWS DataSync can work with multiple EFS, Fsx, and S3.
