How Does Bluetooth Work?
Overview
What is Bluetooth ? It is a technology that uses low-power, short-range communication technology that is used for connecting and sharing data between two or more devices electronically. It is used in a wide variety of applications like headphones, phones, etc.
How Does Bluetooth Work ?
How does Bluetooth work inside a device ?
The working of Bluetooth consists of sending and receiving signals from one device to another. It sends and receives radio waves by using 79 different frequencies in a band of the spectrum which is centered at 2.45GHz, used for avoiding interference.
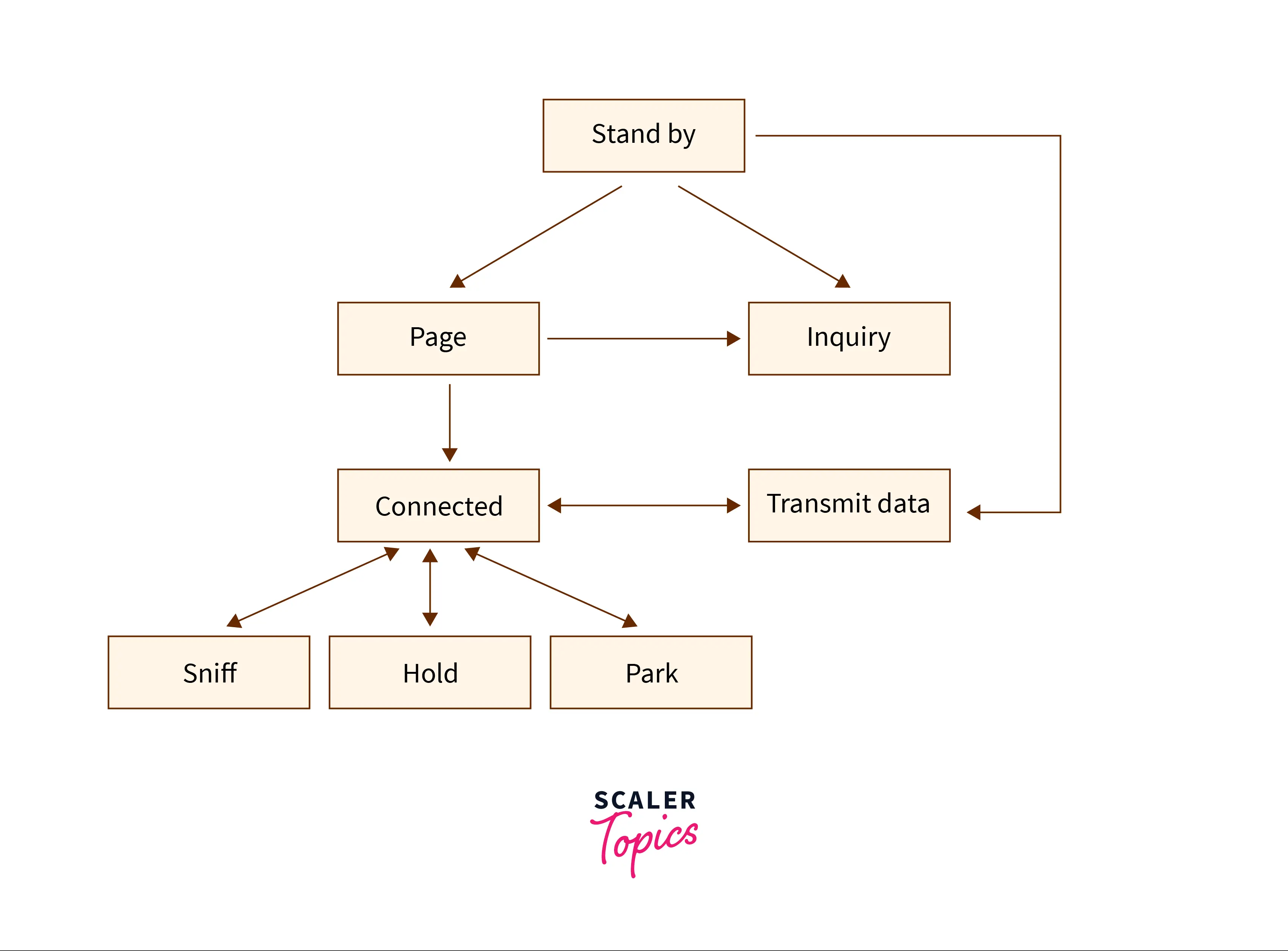
Following is the sequence of working of Bluetooth:
-
Every node determines nearby Bluetooth devices using electromagnetic waves. This process is called "inquiry".
-
If the Bluetooth device wishes to check the information about another device in that range then an inquiry is executed.
-
After the inquiry process, two Bluetooth devices recognize each other one device is in the inquiry state and the other in the scan state.
-
A Bluetooth device in the inquiry state responds to another device. The active devices are detected during the scan.
-
While the connection is the establishment, a page process is followed. Page process is the different types of modes used.
-
If the Bluetooth device wishes to establish a connection, a device enters the page state.
-
Inquiry is used for finding a Bluetooth device with an unknown address same as a page message.
-
Modes when the device is in connection :
- Active
- Hold
- Sniff
- Park
-
In active, the device transmits and receives data packets and controls data.
-
Hold mode is used for restarting the data transfer.
-
In sniff mode, the slave device listens to piconet. The slave device is the one where data is to be sent.
-
In park mode, the device will be inactive.
-
The slave device is assigned a bit address. The hold, park, and sniff are used for power saving.
-
If the slave is inactive, it enters into the park mode. In this, the slave device maintains synchronization with the master. The master device is the one that sends data. It releases the MAC address. Hold and sniff retains this MAC address.
-
For transmission of extensive data, sniff mode is used. It avoids unnecessary transmission of poll packets.
-
Sniff mode has a higher duty cycle as compared to hold and park.
-
For connection establishment, a unique inquiry and page algorithm is used. The paging algorithm is for detecting the mode of Bluetooth whereas the unique inquiry is for resuming the connection of Bluetooth.
-
Let ‘m’ be the master terminal that registers all stand-by terminals. At the inquiry, it becomes a slave terminal.
-
All slave terminals are sent to their master when a ‘PAGE’ message is sent to the slave terminal.
-
This is how data is transferred using Bluetooth.
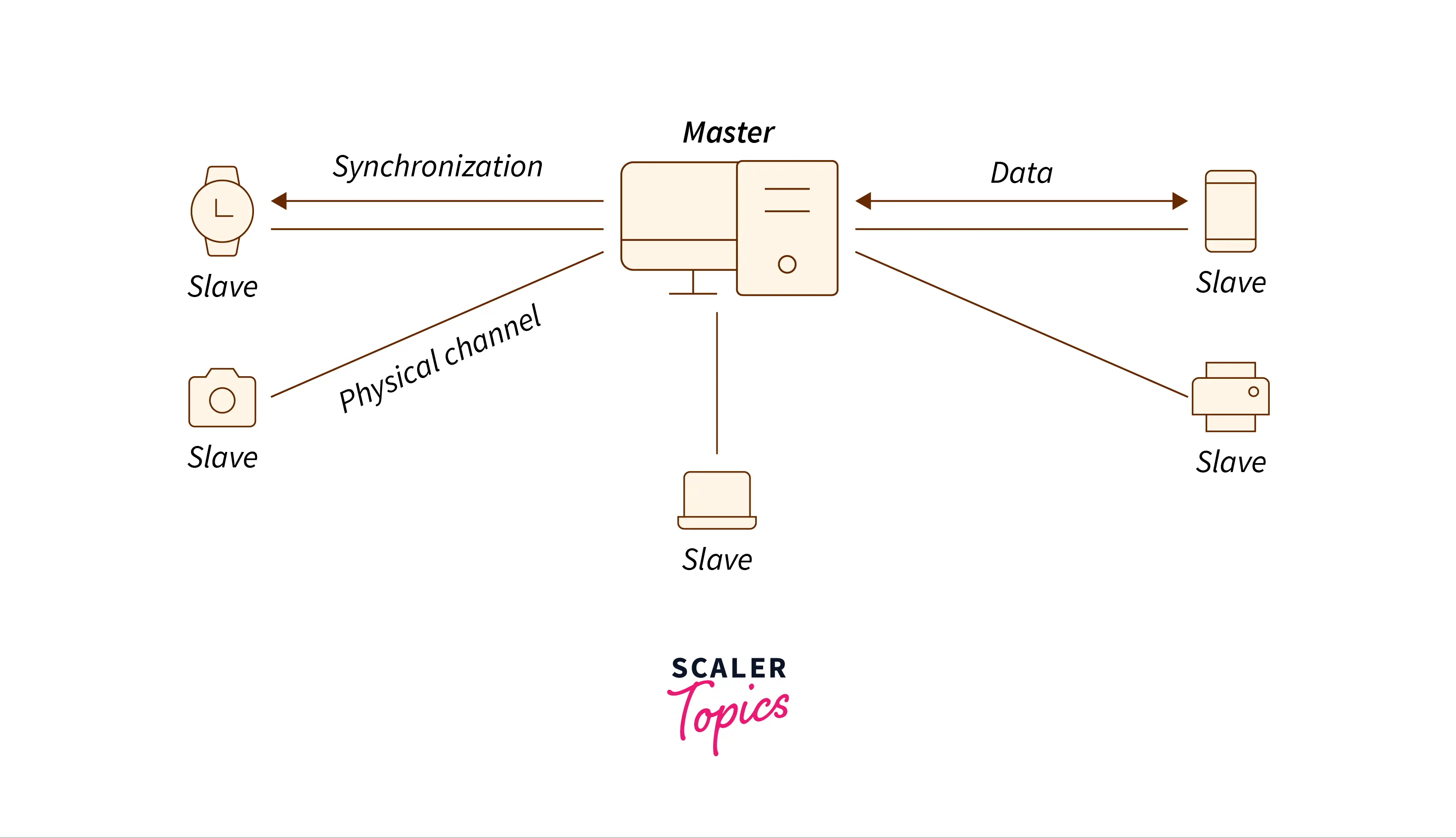
How Does Bluetooth Technology Operate?
The Bluetooth BR/EDR device comes within range of each other, and an electronic form of authentication takes place to test whether the device is secure enough to maintain connection and transfer data. It happens automatically instead of the user manually doing it. If a Bluetooth LE device wants to broadcast a message or packets to all the nearby devices then the process is called advertising. The packets used for advertising or broadcasting contain useful information about the device that is used for sending messages.
The other device will scan to find a suitable advertising device for maintaining connection and data transfer. The scanning of the nearby device is done when the user presses the scan button which means it only scans when the user clicks on the scan button. The user is then presented with a list of nearby devices available for connection and data transfer. The peripherals of Bluetooth be it a smartwatch or headphones are all connected to a common central device to form a PAN, Personal Area Network also knowns as a piconet. Once this is established, radio hop frequencies are used to be connected with a device without interfering with another device. These radio channels avoid interference of waves and this is called adaptive frequency hopping.
Devices Using Bluetooth technology
Following are the devices in which Bluetooth technology is widely used:
- Bluetooth keyboard
- Bluetooth headsets
- Bluetooth-equipped printer
- A GPS device that uses Bluetooth
- Bluetooth-enabled webcam
- Stereo headset
- Television remote
- Wireless speakers
Factors Affecting the Range of Bluetooth Devices
Several key factors affect the range of Bluetooth connection, which includes :
- Radio spectrum:
The Bluetooth technology uses a 2.4GHz ISM band to enable a good balance between throughput and range. The spectrum has a range from 30Hz to 300GHz which means, the lower the frequency, the larger the range and data rate. - The physical layer of the network:
It defines modulation techniques to be used to send the data over a specific band of radio frequency. This includes the detention of error, the number of channels that should be used, their capacity, their guard band to avoid interference, and the effectiveness of utilizing those channels properly. All of these factors together impact the range of Bluetooth. - Sensitivity of receiver:
It is a measure of the minimum strength of the signal that a receiver can interpret. The minimum value for the sensitivity of a receiver is 80 dBm depending upon the network. If the strength is minimum then the distance covered is small too. - Power transmitted:
It defines if the signal can be heard over a long distance or not. The higher the power of a signal, the better it is since it can travel across long distances. - Antenna gain:
The antenna converts the electrical energy coming from the transmitter to electromagnetic energy for ending it to the receiver. For effective gain of the antenna, its type, size, and focusing power should be designed properly. The typical gain for Bluetooth is -10 dBi to +10 dBi. If the gain is less then the range covered is less since there is a loss in signal due to focusing power. - Path loss:
It is a reduction in the strength of the signal as it travels over a longer distance due to atmospheric losses. The reduction occurs due to the absorption of signals by atmospheric gases and hence reduces the range.
Conclusion
- Bluetooth is a technology that uses low-power, short-range communication technology that is used for connecting and sharing data between two or more devices electronically.
- Following is the sequence of working of Bluetooth: Inquiry -> Page -> Connected
- Following are the devices in which Bluetooth technology is widely used:
- Bluetooth keyboard
- Bluetooth headsets
- Bluetooth-equipped printer
- A GPS device that uses Bluetooth
- Bluetooth-enabled webcam
- Stereo headset
- Television remote
- Wireless speakers
- Factors affecting the range of Bluetooth devices:
- Radio spectrum
- The physical layer of the network
- Sensitivity of receiver
- Power transmitted
- Antenna gain
- Path loss
