How Does the Internet Work?
Overview
An internet is a huge network of networks that helps us to connect millions of computers together. These computers that are connected to each other through the internet can interact with each other over the internet.

The Internet operates on a technique called packet switching. In packet switching, the data that is transferred among the different computers on the internet are transmitted in the form of packets. These packets contain information about the error control mechanisms, the address of the destination, and also the sequence in which the packets are to be transmitted.
Nowadays, whatever we do is directly or indirectly related to the internet. We chat with our friends on various social networking websites which actually use the internet to send messages. We order food using different mobile applications which also use the internet.
In this article, we will discuss how the internet works in detail.
How Does the Internet Work? - A Step-by-Step Process
The Internet connects millions of computers to each other so that they can interact with each other and also transmit data to each other.
Have you ever thought about how the internet makes these connections and sends data? Let's discuss how the internet works.
-
Internet uses a packet switching technique to transmit the data. Thus, the data to be sent is divided into packets and the data is sent in the form of packets only. Each packet of data contains various information like the address of the destination, error control information, etc.
-
Internet majorly uses protocols called Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to transmit data from one computer to another.
Internet Protocol (IP) The internet protocol is a network layer protocol that is responsible for defining the rules that define how the information is sent over an internet connection from one computer to another.
Internet Protocol is responsible for gathering the addresses to which the data is to be transmitted.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) The transmission control protocol (TCP) is a transport layer protocol that works along with the internet protocol to transmit data over the internet. It is a connection-oriented and reliable protocol i.e. it establishes the connection first and then only, sends data over the established connection hence, there is no packet loss in the transmission control protocol.
Transmission Control Protocol is responsible for the delivery of data once the Internet protocol gets the IP address of the destination.
-
Also, there are several other protocols that are used by the internet for different purposes. For example, it uses Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to send mail from one client to another, it uses File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to transfer files over the internet, it uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) through which a browser (client) can interact with the internet server.
What happens when we surf the Internet?
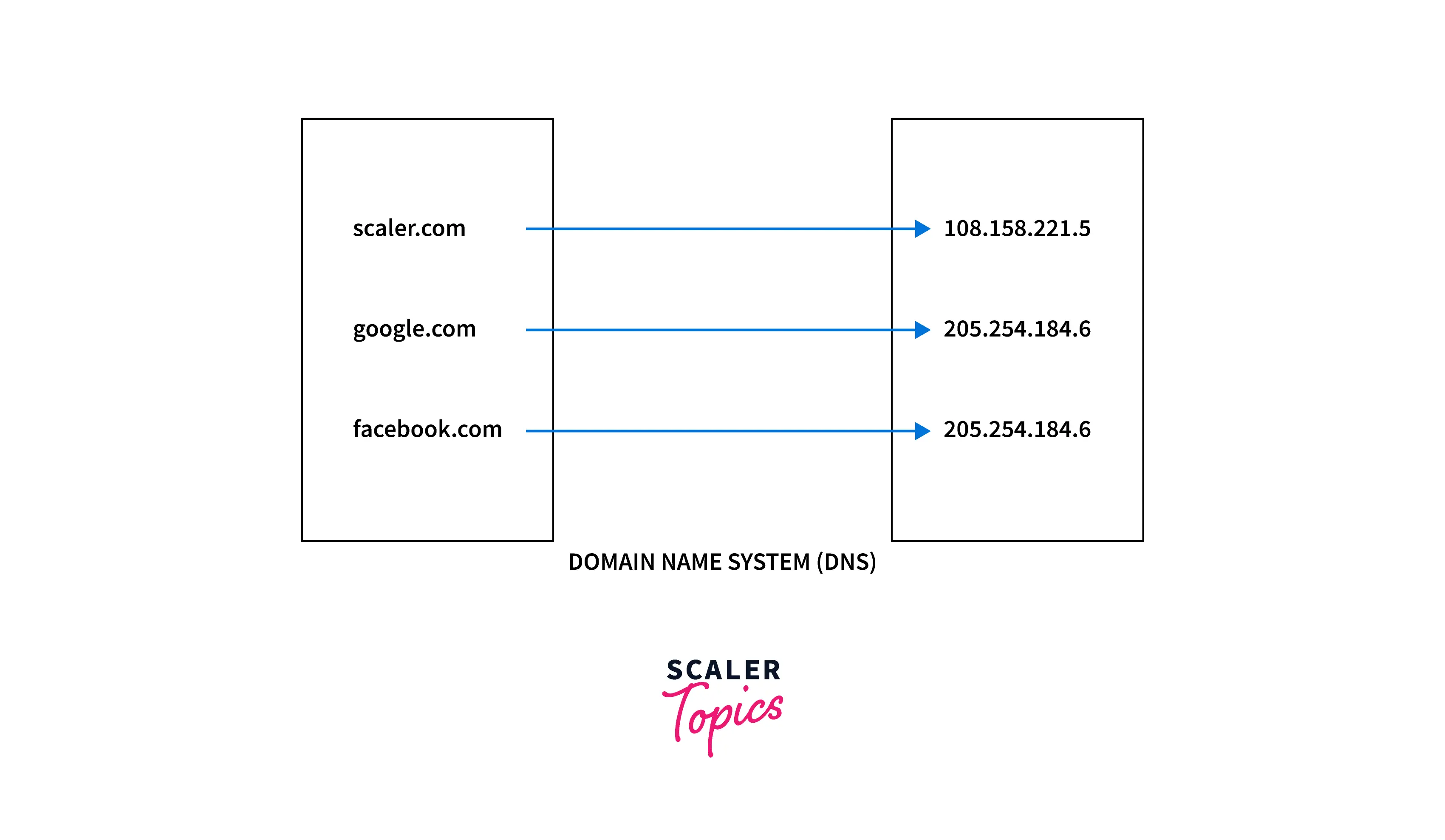
1. Extracting IP address of a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) In our browser, we enter the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) address of the website we want to visit. Once we enter the URL address of the website, the browser with the help of the DNS (Domain Name System) extracts the IP address corresponding to the URL address that is entered. The DNS (Domain Name System) contains the mapping of the URLs along with their corresponding IP addresses.
2. Sending request to the server to access the webpage and receiving response Once we get the IP address of the website we want to access using DNS, the browser sends an HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) request to the server to extract the HTM (Hypertext Markup Language)L webpage corresponding to the IP address. This request is sent over PORT 80 using TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). Once the server receives this HTTP request, it responds back with an HTTP response. This HTTP response consists of the information related to the HTML page corresponding to the IP address of the website.
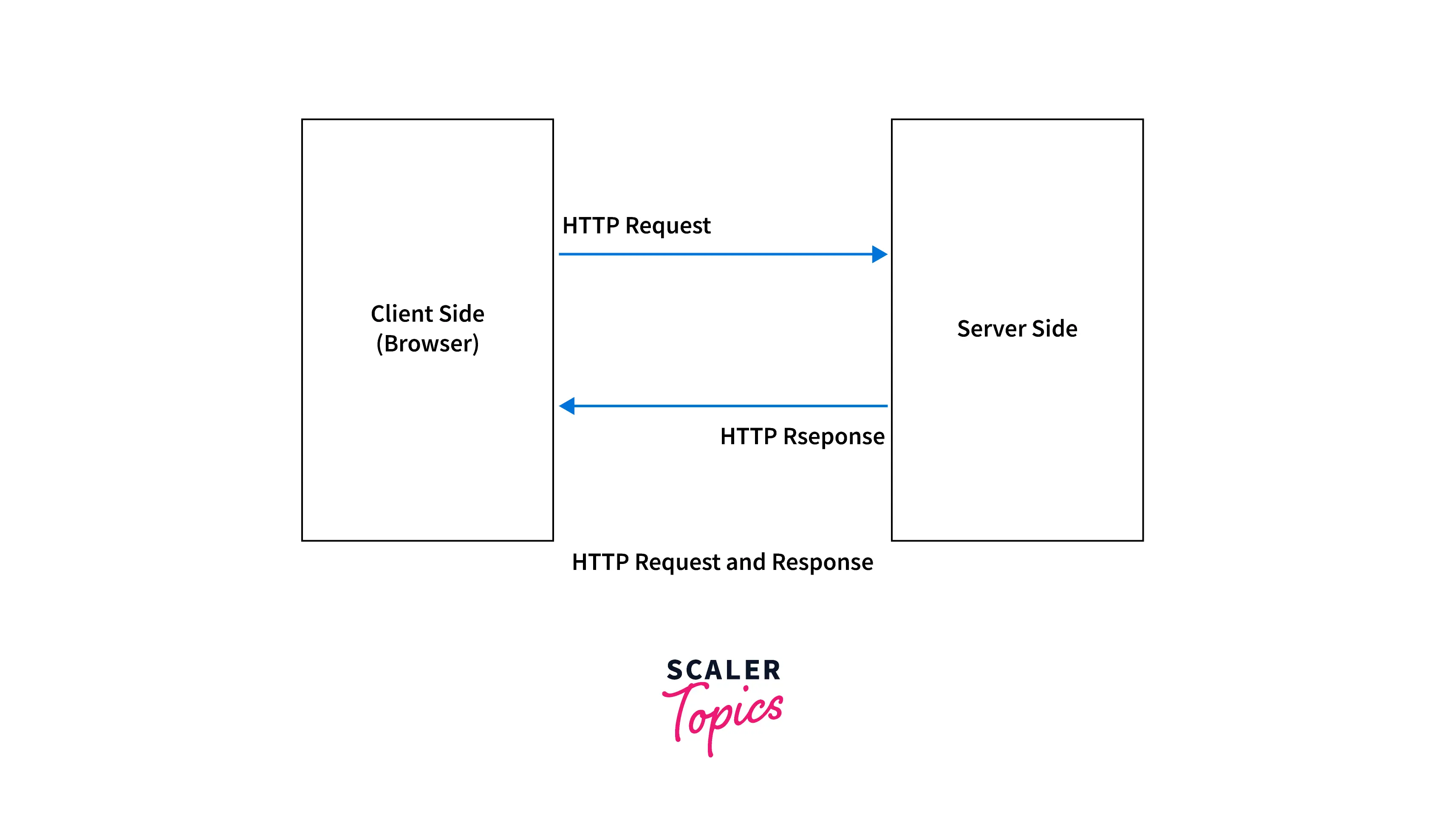
3. Receiving HTTP response and displaying the webpage The browser receives the HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) information for the website along with the response and hence, it processes and displays the HTML page on the browser. Finally, the users can see an HTML page for the URL that they entered.
The Future of the Internet
The information available on the internet is accessed using something known as a web. In the past two decades, there has been tremendous growth in the web. The web has got upgraded from WEB 1.0 (on which, there is only single-side communication between two computers) to WEB 2.0 (which allows two-way communication between two computers). In the past few years, we have seen various applications of the further upgraded version of the web i.e. WEB 3.0 which is also the future of the web and the internet.
Web 3.0 majorly focuses on the data of the users. Various advanced technologies like machine learning are integrated with web applications that use the data of the users and hence, result in a much better user experience. `Blockchain technology is also commonly used in modern web applications.
The future of the internet and the web is more likely to be inclined towards gathering user data rather than only being information-centric.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions related to the working of the internet.
Q. Which protocol is used by the Internet?
A. Internet mainly uses two protocols i.e. Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission control protocol (TCP) to transmit data from one computer to another.
Q. What happens to the URL that is entered into the browser?
A. The browser converts the URL entered by the user into an IP address using the domain name system. This IP address is more friendly to the computer than the URL.
Q. What happens once a browser gets the IP address of a website / How the internet works?
A. As soon as the browser gets the IP address of the website from the DNS (Domain Name System), it sends an HTTP request to the internet server along with the IP address. The server responds back with an HTTP response which contains HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) information about the website. This HTML information is used by the browser to display the webpage to the users.
Q. On which PORT the HTTP request and response is sent and received respectively?
A. HTTP establishes a connection on PORT 80 and hence, the HTTP request and response are transmitted on PORT 80 only.
Dive into the world of computer networking with our Free course designed for beginners. Enroll now and build a strong foundation in networking principles!
Conclusion
- An internet is a huge network of networks that helps us to connect millions of computers together.
- Computers that are connected to each other through the internet can interact with each other over the internet.
- Internet uses packet switching technique to transmit the data. Thus, the data to be sent is divided into packets and the data is sent in the form of packets only.
- Internet uses protocols called Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to transmit data from one computer to another.
- When a URL is entered in the browser, the browser converts it into an IP address using DNS. HTTP requests and responses are sent from the browser and server respectively and hence, the HTML information corresponding to the webpage is received by the browser. The browser displays the webpage using this received HTML information.
- The HTTP request and response is transmitted on the PORT 80.
