Types of Network Topologies
Overview
Networking has become an essential component of cybersecurity & all of the daily activities we perform while communicating with the internet. Any communication network our phone or system lies in follows or comes under a structure called the topology. This article will discuss network topologies, their types, and troubleshooting topologies with software.
What is Network Topology?
Network topologies or topologies of the internet architecture define the structuring of computer networks or how various network components within the computer are connected. In other words, they are the arrangements of different network nodes and connected lines. The term topology was derived from the Greek words – "topo" which means "place" and "logos" which means "to study."
Why is Network Topology Important?
Several reasons make network topologies an essential part of computer networks. It plays an indispensable role in determining how well your network is functioning. Based on your organization's requirements, choosing the most appropriate topology will help increase the internal performance of the network. Besides, having a good understanding of the topology benefits in locating faults. If the network engineers have a clear insight into the entire topology, they can protect the network from unnecessary downtime. Apart from troubleshooting errors, an appropriate diagram/planning of the network topologies also helps allocate resources & network devices effectively.
Network engineers and IT administrators are mainly responsible for designing network layouts within an organization. Fine-tuned network topologies & strategically designed network architecture help increase data efficiency, which can, in turn, help to minimize maintenance & operating costs. The diagrams that you will see in this article are the simplest versions of these network topologies. The arrangements of network layouts determine whether these network functionalities will make or break.
Types of Network Topologies
Network topologies are of two categories - physical and logical. Before digging deep into the concepts, here are the types of physical topology in a diagrammatic format.
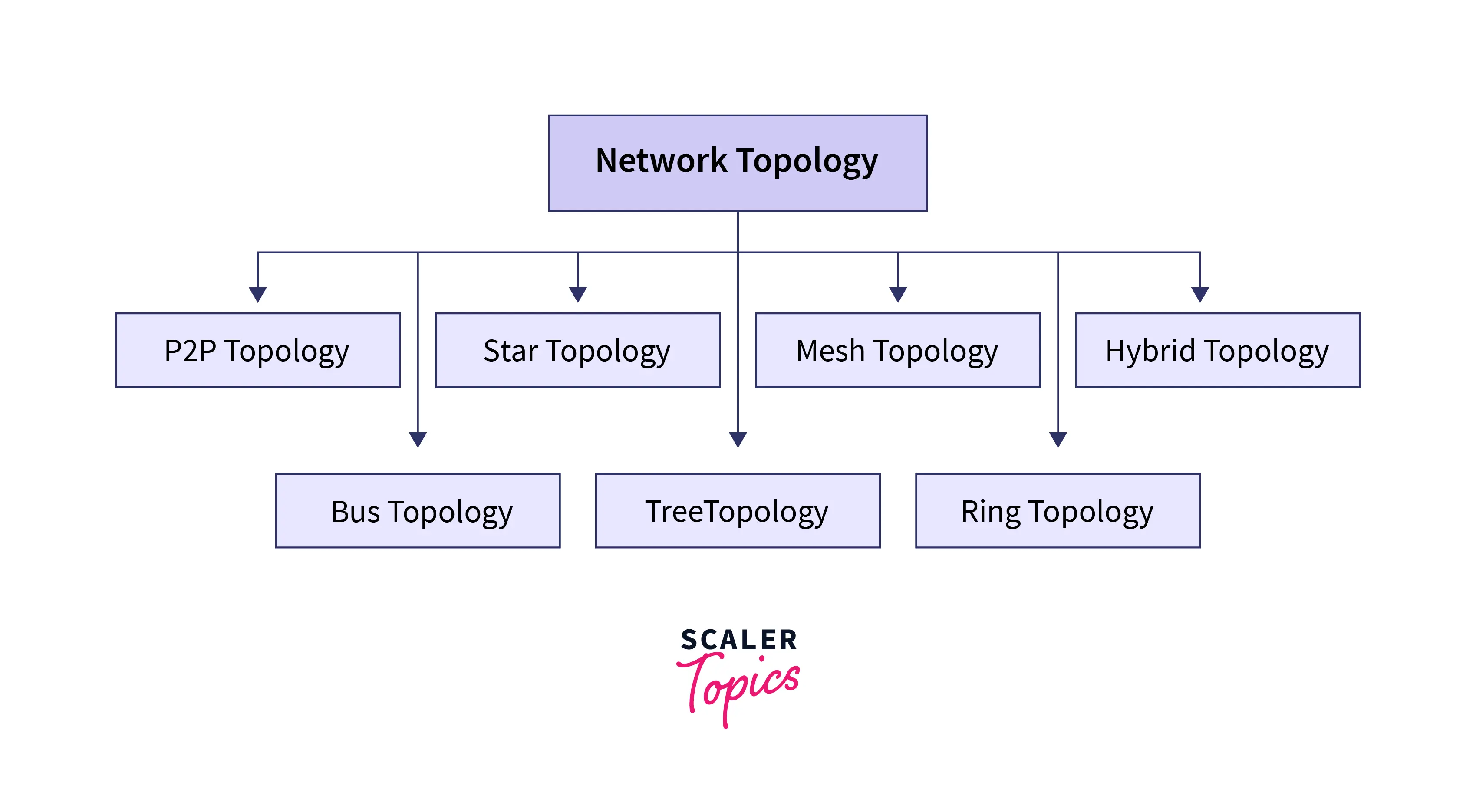
Physical Topology
It determines the actual connection through which the computer and other associated nodes within the network remain connected. These are physical connections of cables and wires with proper arrangement of devices and nodes along with specific configurations. There are seven different types of physical topologies. These are:
1. P2P topology: We can expand P2P as a Point-to-Point network topology. It is the simplest topology wherein two nodes, computers, or other network devices remain connected to each other directly through a piece of cable. The most obvious scenario for creating a P2P network is connecting two computers via an Ethernet cable (twisted pair cables like UTP Cat 5e, STP Cat 6e, etc.) in the RJ-45 port.
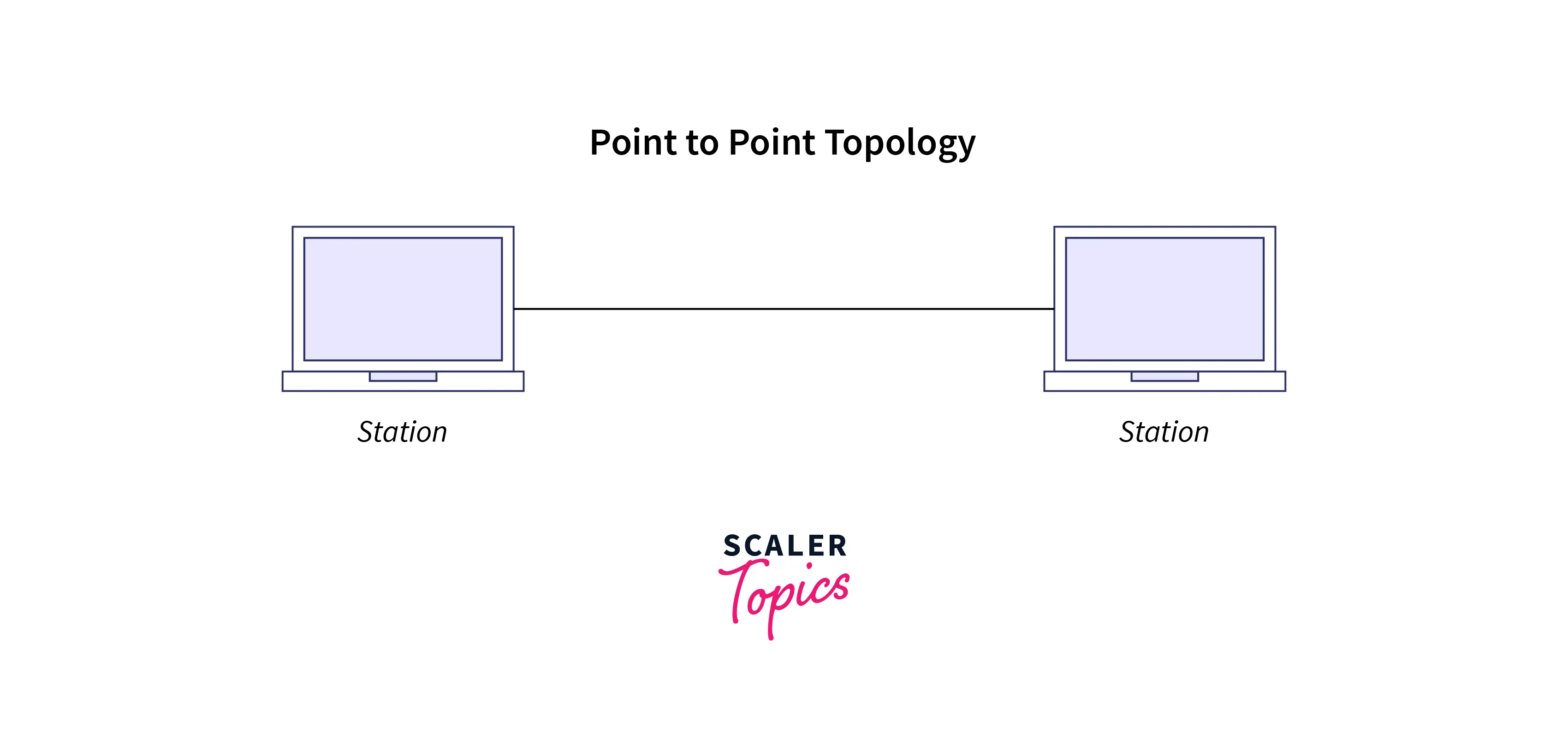
-
Advantages of P2P Topology:
- The construction and maintenance cost of this overall topology is very inexpensive.
- Since the P2P network is not dependent on any centralized system, the two nodes or computers can independently function with each other.
- It does not require advanced knowledge to set up or design network topologies.
- Troubleshooting is the easiest in such topologies.
- Because of its straightforward structure with limited one-to-one connectivity, the performance of such topology remains the maximum.
-
Disadvantages of P2P Topology:
- The resources within the network are not centrally stored and thus are not organized.
- The security postures in P2P topology are very limited.
- There is no way to back up network resources and files, which make them prone to infection by virus or other malware.
- P2P network activities might expose your confidential details or private information.
2. Bus topology: It is another simple network topology where the topology uses a common bus or cable called the backbone to connect all the nodes within the communication system. It uses tap devices to connect drop lines through which all other computer systems get connected. This network topology also adds terminators installed at each end of the backbone to avoid the reflection of signals.
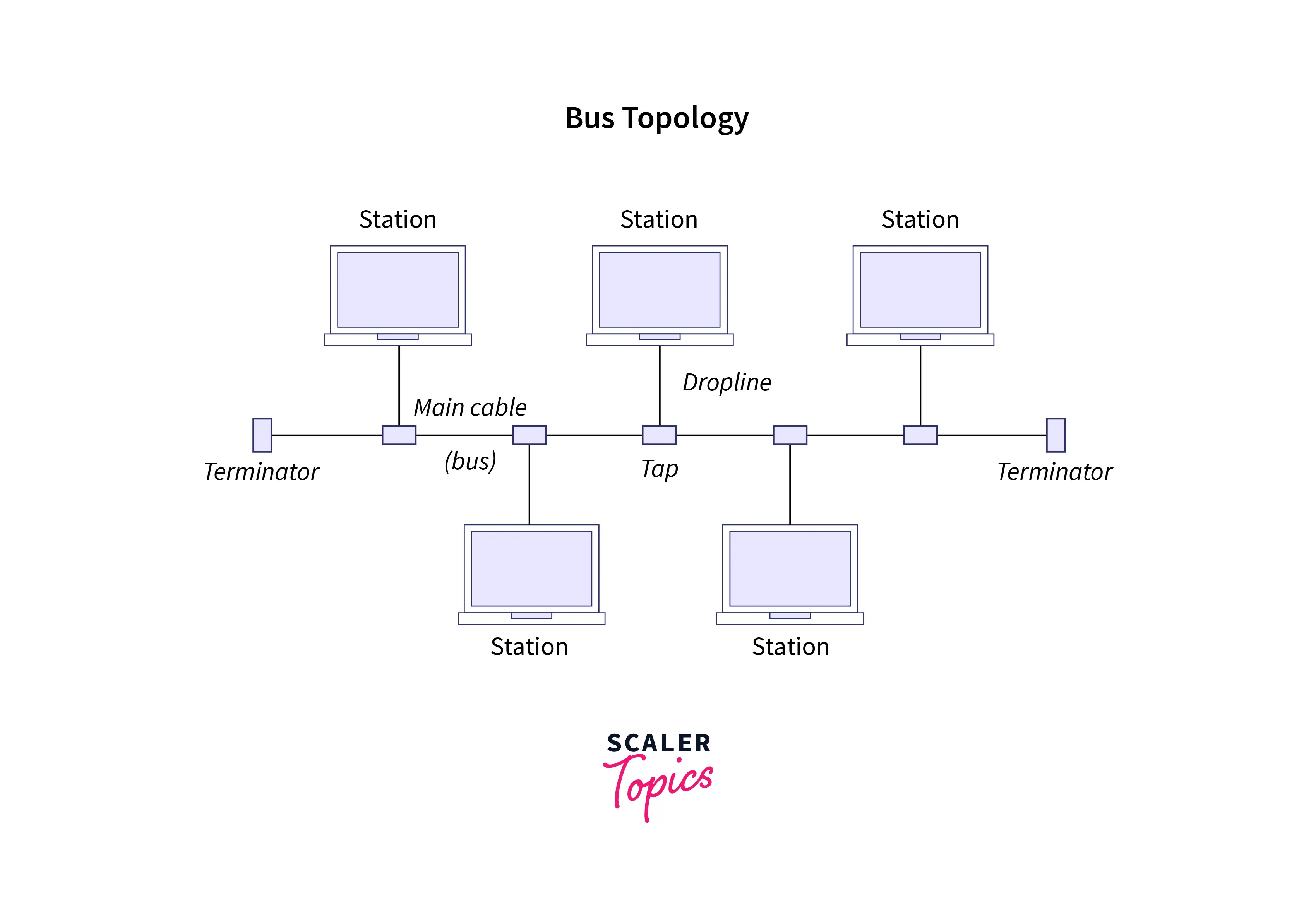
-
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- It works efficiently when the network is small.
- The length of the bus topology is less than that of other network topologies.
- It is easy to configure due to its simple design.
- Understanding bus topology is easy.
- Expansion is easy just by joining two cables together.
-
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:
- If the backbone fails, the entire network topology fails.
- It is not the right choice when it comes to designing large networks.
- Troubleshooting individual devices and their associated cables becomes a minor challenge.
- Adding unlimited devices to the backbone often slows the entire topology.
- Data packet loss remains high in bus topology.
3. Ring topology: As the name suggests, the ring topology is circular and is a modified version of the bus topology. In this topology, all the system remains connected to the other system on either side. In other words, there will be two neighbors of the station. The data transmission occurs in one direction, making the entire network act as a half-duplex. In a dual ring topology, the data transmission occurs bi-directional.
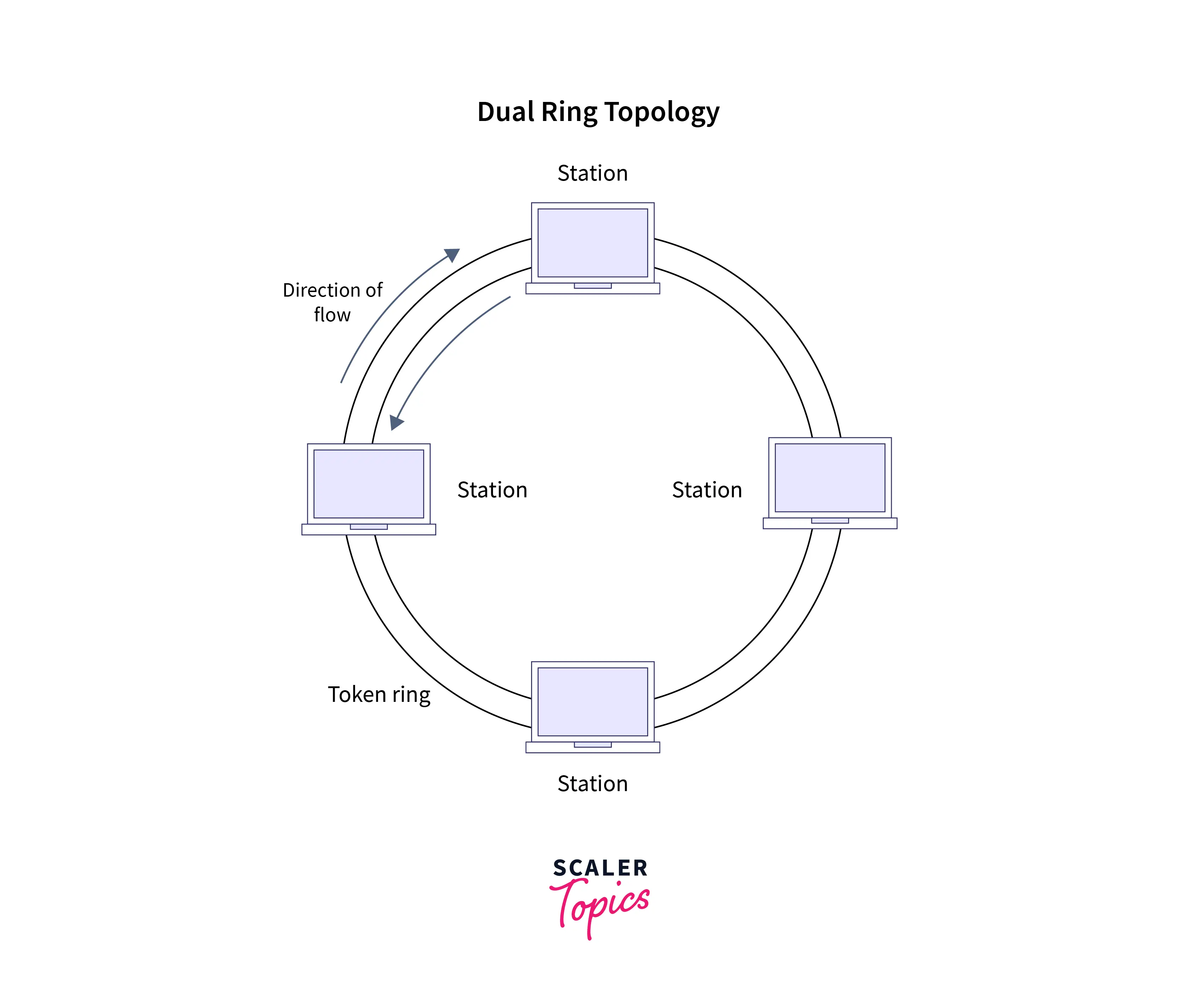
-
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- All the systems within the network get equal access to the resources.
- It is less expensive to design this topology and expand it.
- Even if the traffic grows, the token passing technique increases the performance of ring topology.
- It is easily manageable.
- The topology remains organized in a proper order, which makes it easy to understand.
-
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
- Since it follows a unidirectional data flow, data packets should pass through all the nodes.
- Adding or removing a node is difficult when the network is active. It might also cause issues in the network.
- Once the ring topology gets created, it is not feasible to scale the design by adding new nodes.
- For communication of one computer with the other, all the computers within the network should remain on & active.
- Each device requires two ports, which may not always be there.
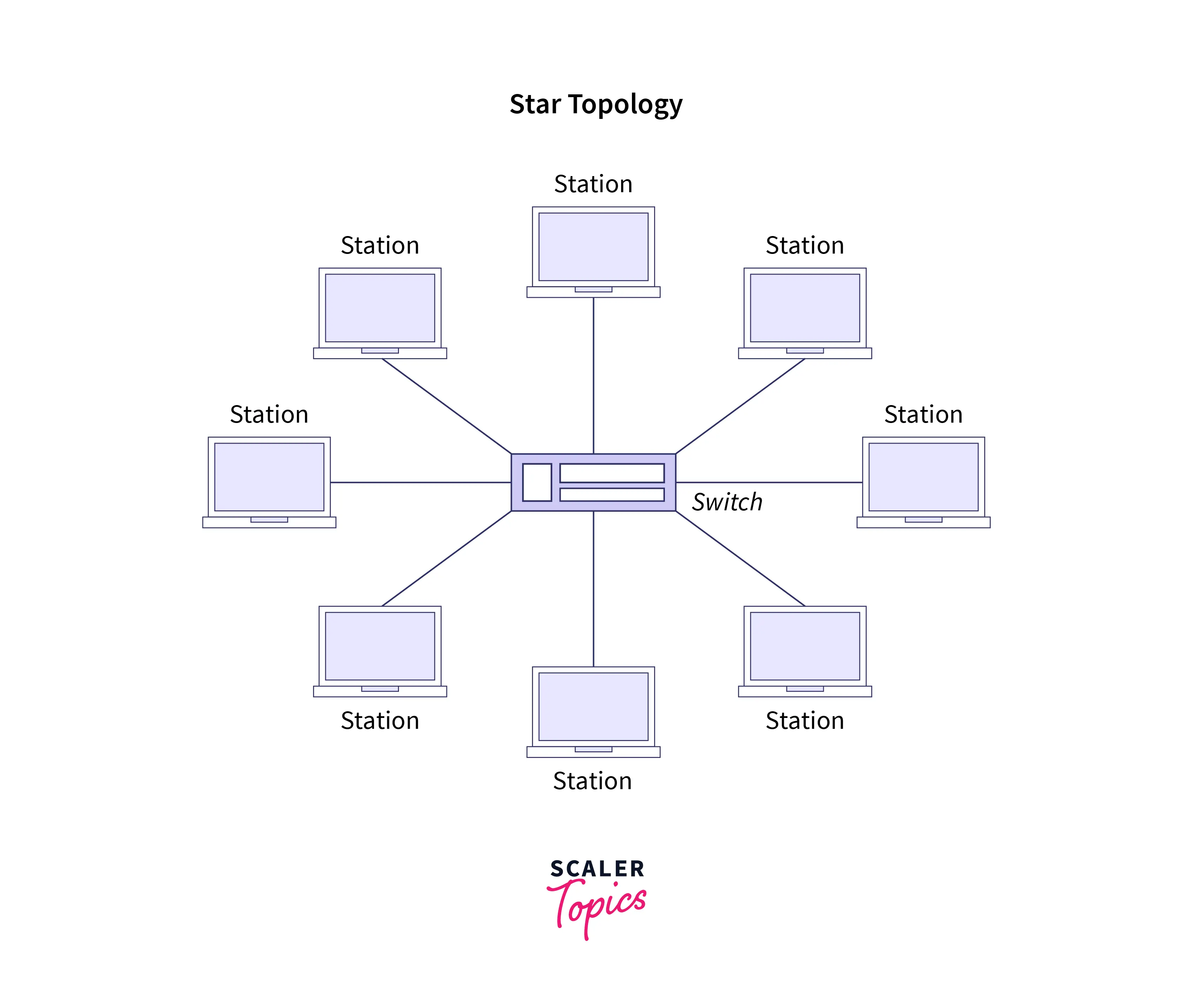
4. Star Topology: It has become one of the most straightforward & most prominent network topologies. It is widespread because of its several advantages. The topology has a centralized system, usually a switch, which contains multiple ports to connect one system or node with the other. In this topology design, no direct connection resides between the two systems. All the communication between multiple systems goes via the switch (central unit). If any system fails to connect to the centrally located unit/device, it does not impact other systems connected to it.
-
Advantages of Star Topology:
- No data collision occurs in this topology. That makes star topology a high-performing topology.
- It is very reliable because of its straightforward design structure.
- Fault detection is also easy.
- Each device requires only one port.
- If one system or station disturbs or becomes faulty, it does not affect other systems within the topology.
- Scalability becomes easy.
- This topological design is less expensive because it requires limited cables and ports.
- Understanding and troubleshooting such a topology is also easy.
-
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- If the central device fails or gets corrupt, the entire network goes down or becomes useless.
- The central system (Hub or Switch) requires more maintenance because of its maximum utilization.
- A hub instead of a switch can reduce the device cost but leads to privacy compromise (because the Hub does broadcasting).
- It requires extra hardware (usually a Hub or Switch) that might make the topology costlier than the ring topology.
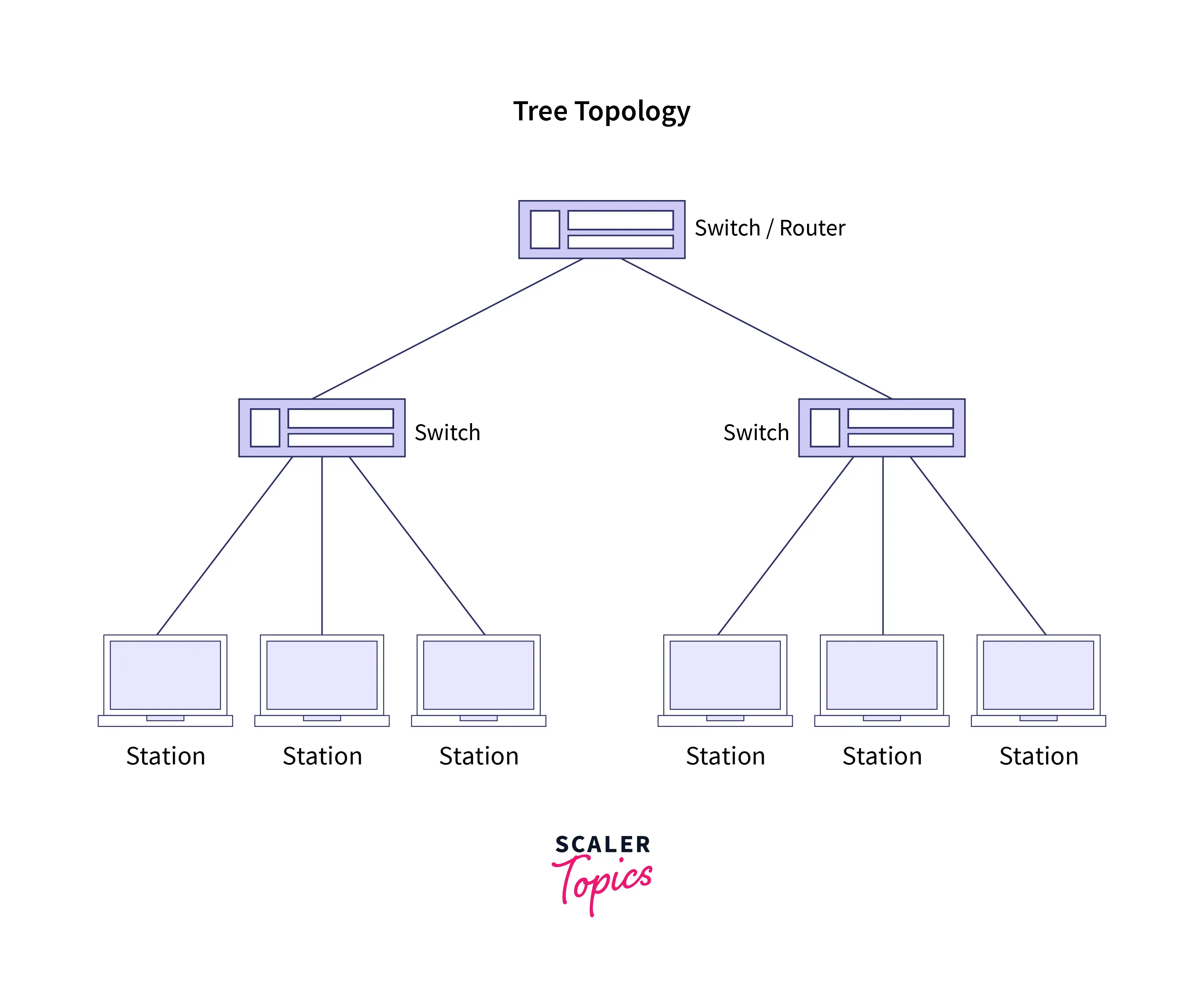
5. Tree Topology: This topology is an extended version of the star topology and uses a hierarchical tree-like structure by branching into a more complex network. Designing and maintaining a tree topology is easy and is suitable for large networks. Because of its high scalability and easy-to-troubleshoot feature, large enterprises and organizations use it to design their networks.
-
Advantages of Tree Topology:
- Lots of network device vendors support such a topology.
- It follows a hierarchical approach with a centralized arrangement of data.
- It leverages point-to-point wiring for individual segments, making the topological design straightforward.
- The Wide Area Network (WAN) leverages this topology for efficient communication.
- Networks created using the tree topology are reliable.
-
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
- Configuring such a massive topology often becomes difficult.
- The segment length is limited & the segment limit relies on the type of cables utilized.
- It requires a large number of cables, which makes it costlier compared to other topologies.
- It requires two or more network devices to make them the centralized unit. It counts additional costs to the entire network.
- Often the backbone or the top-most central device (switch) emerges as the failure point for the entire network segment.
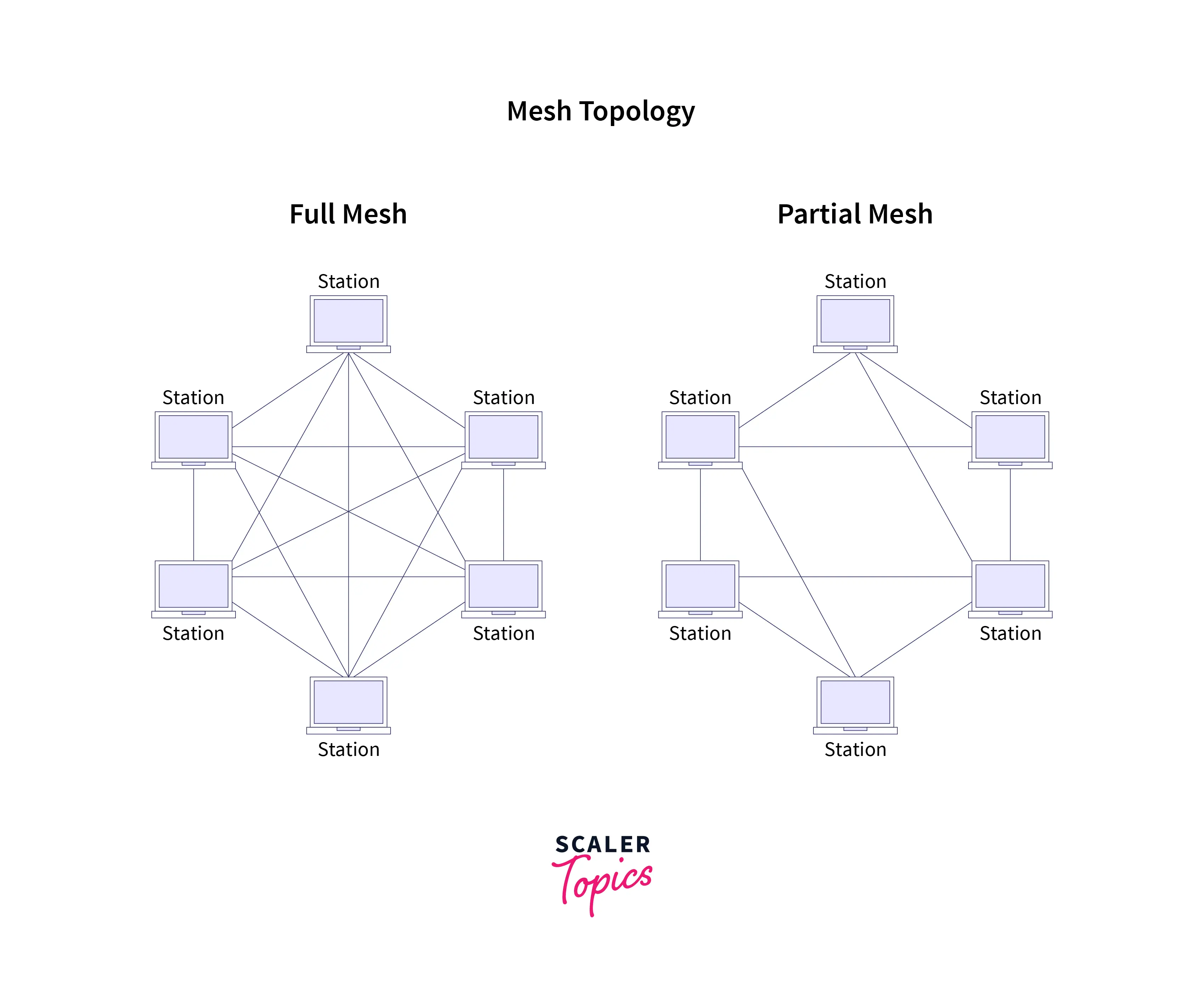
6. Mesh Topology: In this topology, each node or system can connect to the other directly and indirectly. Network administrators can set multiple paths (directly or indirectly) to connect two or more systems. Mesh topology is of two types:
a. Full mesh: In this connected mesh, each system remains connected to all other systems within the network.
b. Partial mesh: In this connected mesh, at least two systems will remain connected to all other systems.
-
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- If a single device or system fails, it won't impact or break the network.
- This topology is robust enough to withstand any topological issues or situations.
- If any wiring fails, multiple other wirings keep one system connected to the other.
- Including a new device does not disrupt standard data transmission.
- It is very straightforward to identify faults.
- This topology does not face traffic problems as all the nodes remain connected with dedicated point-to-point links.
- Communication remains fast because of point-to-point connectivity.
-
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- Installation and configuration are intricate in this topology.
- It is costly because it requires a massive amount of cables.
- It consumes more power because all the different nodes have to remain alive/active to share the load.
- Maintenance is a challenge in this topology.
- There is a high possibility of having a redundant connection.
- In an enterprise scenario, because of such massive connectivity, it takes a larger space to install and set up such a network.
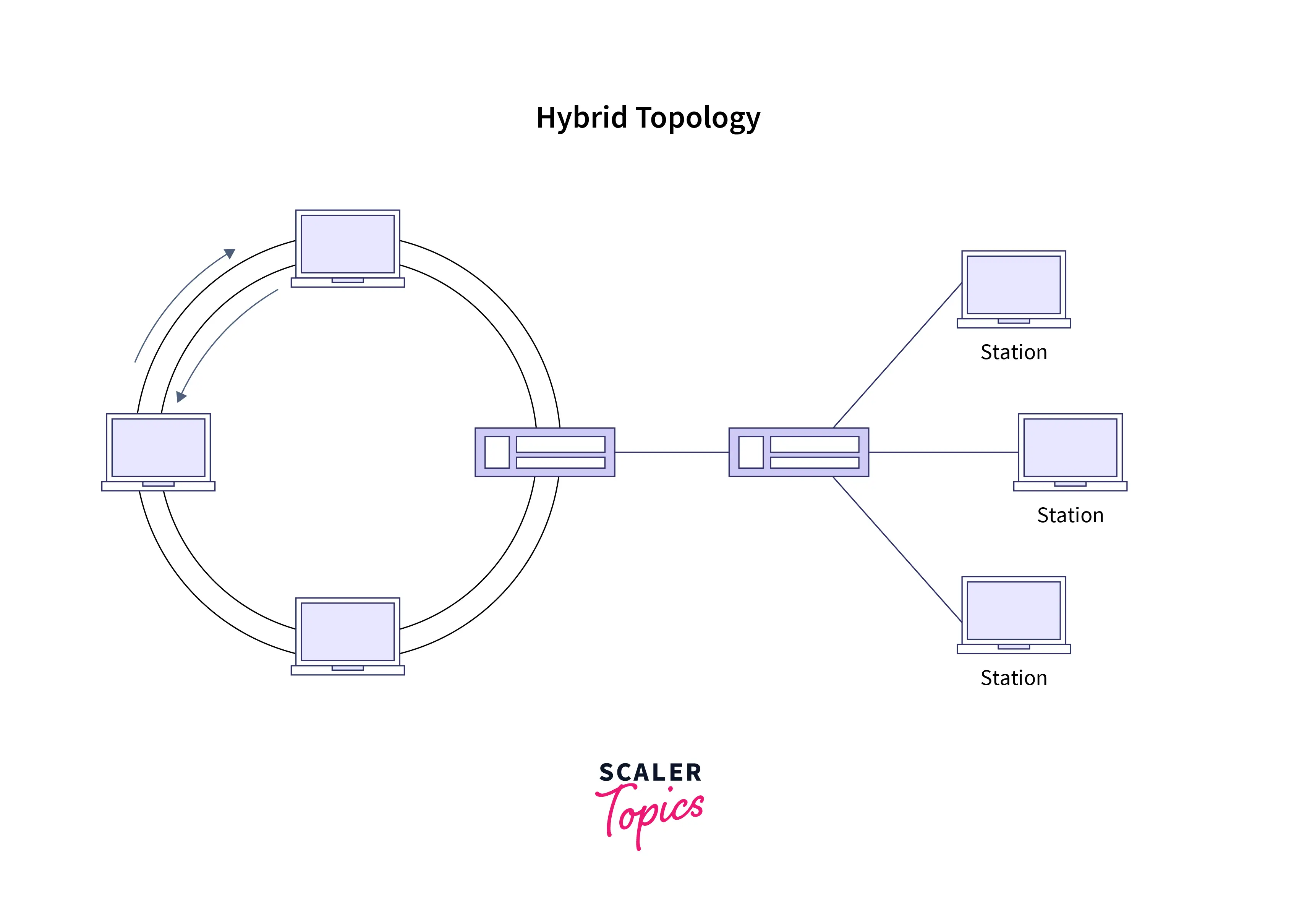
7. Hybrid Topology: Hybrid topology, as the name suggests, is a mixture of two or more mentioned topologies. Network engineers and administrators prefer to leverage the benefits of different topologies into one using the hybrid topology. Practically, it is the most widely implemented topology. It gives flexibility to the network administrators to determine which topological combination to use, depending on the requirement.
-
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Such topologies are flexible to implement and configure.
- By combining the different topology types, network architects and engineers can leverage the benefits of multiple topologies wherever necessary.
- It has the potential to endure a large volume of traffic.
- The speed of the topologies went faster when two or more topologies were appropriately configured.
- They help create large enterprise networks with full customization.
-
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Often appending more and more topologies of different types makes the entire hybrid topology complicated.
- Such topologies are more expensive than any other topologies mentioned in this article.
- Often, such topology requires changing the hardware to connect one topology with the other.
- As the network grows, it becomes challenging for the network administrators to keep all the aspects of the topology functionally optimal.
Logical Topology
Logical topology deals with the higher-level architecture of how the network is set up & operates. It represents how data flows from one system to the other. In other words, the logical topology explains how data will transfer over physical topology. Accessing and leveraging the virtual network and cloud resources also comes under the logical network topologies.
Performance Troubleshooting
Network architects and administrators must check the overall performance of the topology after designing them and periodically. It will help keep track of different network issues, performance glitches, and outages. They can use various third-party software like Solarwinds network management software or Datadog Network Performance Monitoring to check the network performance baselines. Such software delivers a vivid picture of how the network segments behave when they are healthy.
If your network topologies are complex, it might be challenging to identify which network component performs abruptly. Performance managers & network monitoring software can yield a comprehensive view of the network topology. It can give a clear idea of the entire network in a one-map outline and where the fault has happened.
Conclusion
- We hope this article has highlighted a comprehensive view of topologies and their types.
- This article also showed the advantages and disadvantages of each one of them.
- Network professionals and researchers recommend network architects leverage the network topologies with which they are more familiar.
- The article also highlighted why network performance troubleshooting is essential and the names of software that can help identify issues in the network topologies.
