How to Learn AI in 2025: Step-by-Step Roadmap from Beginner to Expert
Every other person, just from the sound of AI, thinks of ChatGPT. Ever wondered why?
That’s because it is the most convenient tool that is used by a majority of people. Hence, a lot of people equate AI to a tool that helps here and there, but if you are someone exploring the world of computer science, you would surely know there is more to it.
\What if we tell you AI has been prominent since the 1950s? Back then, researchers like Alan Turing were already asking whether machines could “think.” In the 1960s, a chatbot named ELIZA could carry on a conversation that felt surprisingly human for its time. By the 1970s and 80s, industries were using expert systems like MYCIN to support medical diagnoses. The 90s gave us a breakthrough moment when IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov, proving machines could take on human intelligence in strategy games.
As technology advanced, AI slowly moved into our daily lives. Spam filters, Amazon recommendations, and Google Maps navigation were all powered by AI long before ChatGPT existed. Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant made AI even more familiar.
And a career revolving around AI in 2025 is surely a promising choice.
Let’s explore how to learn AI throughout the blog!
Why Should You Learn AI in 2025?
Proficiency in AI for any field can give a sudden boost to your profile; the demand is surging and is predicted to increase in the coming years.
Here’s why choosing AI in 2025 can be a smart move:
High demand in India
According to NASSCOM, India’s AI market is projected to touch $8 billion by 2025, growing at nearly 40% CAGR.
Job postings for AI roles in India are increasing rapidly, especially in places like Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Pune.
Companies in healthcare, fintech, edtech, and retail are actively hiring AI professionals.
High Salaries and Growth
Entry-level AI engineers earn around ₹6-10 LPA.
Mid-level professionals often make ₹12-25 LPA.
Senior specialists in NLP, machine learning, or data science can cross ₹40-50 LPA.
These are speculative salary ranges and can change in accordance with the company size, place of work, and many other factors.
Global opportunities
In the U.S., AI engineers earn an average of 200K-300K.
Globally, job postings for AI roles have been expanding; there is an indication that AI in US job listings is expected to go up by 56.1% and a 54% jump in AI and ML jobs.
Multinational companies increasingly outsource AI talent to India, creating cross-border career opportunities.
Use of AI across industries
The good thing is that the use of AI is not just limited to the IT industry; it has expanded across almost every sector. Some examples include:
- Healthcare
Companies like Apollo Hospitals and Niramai (a Bengaluru-based startup) use AI for early cancer detection and medical imaging. Global players like IBM Watson Health apply AI for diagnostics and drug discovery.
- Finance
HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank deploy AI-powered chatbots for customer service and fraud detection. Globally, J.P. Morgan’s COIN platform analyzes legal documents in seconds, saving thousands of work hours.
- Retail & E-commerce
Flipkart uses AI for personalized recommendations and supply chain optimization. Amazon relies on machine learning for product suggestions, dynamic pricing, and inventory management.
- Education
BYJU’S leverages AI-driven adaptive learning to personalize student experiences. Globally, platforms like Coursera and Duolingo use AI to adjust content based on learner progress.
- Gaming & Entertainment
Dream11 uses AI to personalize fantasy sports recommendations for users. Netflix and Disney+ Hotstar employ AI to recommend shows, optimize streaming quality, and even develop content strategies. Game developers like Electronic Arts (EA) and Ubisoft use AI to create smarter NPCs and immersive game environments.
This is exactly why How to learn artificial intelligence has been a question lingering in many people’s minds these days.
Also, industries like agriculture, logistics, and even government services are adopting AI rapidly.
Here you can see the surge in demand for AI Jobs from 2018 to 2024
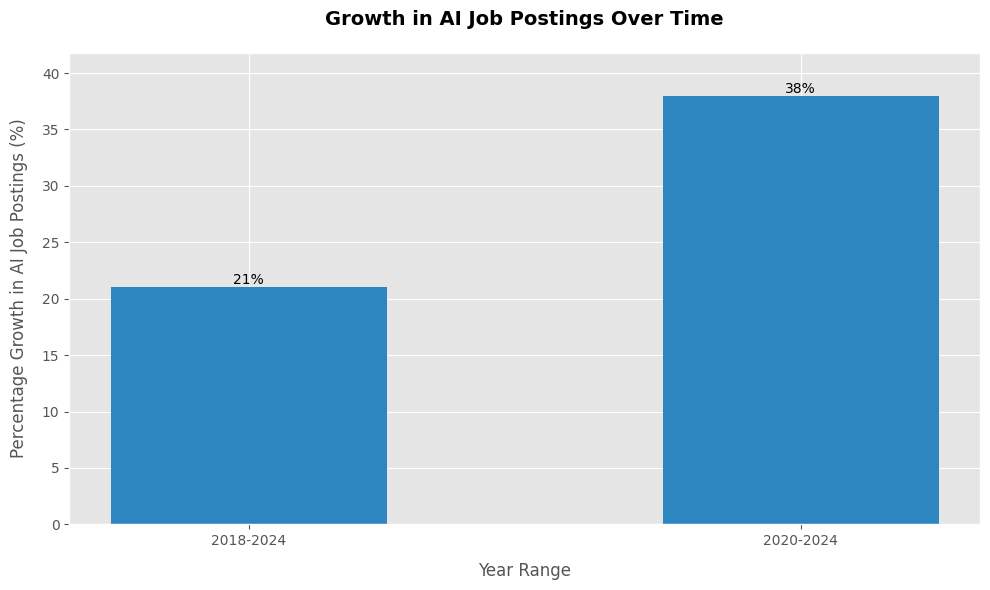
Source: Growth in AI Job Postings Over Time: 2025 Statistics and Data | Software Oasis
Prerequisites to Start Learning AI
You will have to learn AI from scratch if you are new to this field. So, if you’re wondering how to learn AI and where to start, then do go through the list below.
Here's what you’ll need and why:
Mathematics & Statistics
A solid grasp of these mathematical disciplines is critical. Here are some topics to stress upon:
-
Linear Algebra: Practicing matrices, vectors, and operations like multiplication, this will help with neural networks and dimensionality reduction.
-
Probability & Statistics: Key concepts like distributions, regression, and statistical significance provide support for models to interpret data.
-
Calculus (basic level): Knowing how derivatives and gradients work gives insight into how models, especially neural networks, learn via backpropagation.
Programming Skills
-
Python: Having knowledge of Python is still effective, and because of libraries like NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, it is still plenty accessible as well. Also, try to learn Python with AI tools supporting it to acquire a better skill level.
-
Optional tools: Knowing R or SQL is helpful for data handling or analytics workflows.
Data Structures & Algorithms
Understanding how data is organized and processed makes your AI code more efficient. Essential structures include arrays, trees, lists, and graphs, while algorithmic thinking improves model performance.
Basic Data Handling
You'll regularly work with data, so hands-on comfort with:
- Excel and SQL for tabular data.
- Python libraries like Pandas and NumPy for cleaning, transforming, and analyzing datasets.
Seems overwhelming? Don’t worry, below we have provided a mini AI starter checklist. You may use it as it is or make changes according to your plans! Also Read: Artificial Intelligence Vs Data Science: Learn Key Differences
Mini “Starter Kit” Checklist for Beginners Here is a list of basic tasks that can help you begin your journey:
| Task | Details |
|---|---|
| Brush up on Math | Cover linear algebra (matrices, vectors), probability, statistics, and basic calculus (derivatives, gradients). |
| Learn Python Basics | Variables, loops, functions, data types, then move on to NumPy, Pandas, and visualization. |
| Explore AI Libraries | Practice with TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras, or scikit-learn. |
| Understand Data Structures | Learn about arrays, lists, trees, graphs, and how they affect algorithm performance. |
| Practice Data Handling | Use Pandas for cleansing and exploring datasets. Try SQL queries or Excel for simple data tasks. |
| Start a Small Project | Pick a mini-problem, like predicting housing prices or classifying news, and apply what you’ve learned. |
| Iterate & Learn | Revisit weak spots, join AI communities, and keep building more complex projects over time. |
Learning AI might seem scary, but with the right guidance and mentorship, you will be able to make a steady journey towards your goal.
Our students have also mentioned that learning is challenging, but once their course is complete with us, they leave fulfilled and upskilled.
Let’s get more into AI learning, shall we?
Step-by-Step Roadmap to Learn AI
Learning AI can feel overwhelming at first, but if you break it down into clear, manageable steps, the journey becomes much easier. Here’s the AI learning roadmap to guide you from beginner to advanced, with the skills, tools, and resources you’ll need along the way.
Step 1: Learn the Basics of AI & ML
If you’re just starting out, it would be best to first understand the basics and foundation of how AI works. You can begin with the different types of AI, from systems that only do one task to the future concepts of AGI and ASI, then move into core machine learning ideas like supervised and unsupervised learning. At this stage, it’s also worth brushing up on Python and a bit of math; these are the building blocks that will help you move faster later.
For learners who want structured guidance instead of piecing everything together from free resources, Scaler’s AI/ML program usually starts with these foundations, including Python essentials, math for ML, and ML intuition, so you build confidence before taking on deep learning or advanced projects. Here is what you should cover:
Types of AI
ANI (task-focused), AGI (human-level), ASI (superintelligence).
Core ML concepts
- Supervised learning, i.e, regression, classification.
- Unsupervised learning, which includes clustering, dimensionality reduction.
- Reinforcement learning means learning from rewards.
Mathematical grounding
Linear algebra, probability, calculus basics.
Programming basics
Python, NumPy, Pandas.
Project Idea
Train a simple regression or classification model, you can even sign up for bootcamps or voluntary online projects to build your work portfolio.
Step 2: Master Core AI Skills
Once you’re completely confident with your basics, you will now be able to practice core components. This stage is about moving from knowing what AI is to actually building models that can learn from data and make predictions.
In this stage, you’ll cover machine learning first, then further learn deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. Don’t worry if these terms sound overwhelming right now; the best way is to take it one step at a time and practice with small projects along the way.
Scaler’s AI/ML program provides this learning in a way that’s easy to follow. For example, you start with ML concepts like regression and classification, then progress into deep learning with neural networks, and finally tackle cutting-edge areas like transformers and GenAI. This step-by-step approach ensures you’re not skipping fundamentals.
Core skills to master in this step:
Machine Learning (ML):
- Regression for predicting continuous values.
- Classification for categorizing data.
- Clustering for grouping similar data.
- Feature engineering and model evaluation.
Deep Learning (DL):
- Learn Neural networks, i.e, perceptrons, multilayer networks, etc.
- CNNs for image-related tasks.
- RNNs & LSTMs are used for time series and sequential data.
- Transformers for modern NLP & GenAI backbone.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Text cleaning, tokenization, and embeddings.
- Sentiment analysis basics.
- Working with pre-trained models like BERT or GPT.
Computer Vision (CV):
- Image preprocessing
- Object detection & recognition.
- Face detection and OCR as beginner projects.
Projects to try in this stage:
- Build a spam classifier (ML).
- Train a CNN to recognize digits (MNIST dataset).
- Create a simple sentiment analysis model for tweets.
You should try checking out courses that include both learning and projects, along with mentorship for well-rounded support.
Step 3: Work With AI Tools & Frameworks
After getting your core skills in place, the next step is learning the tools and frameworks that make AI practical.
These tools help you clean data, build models, experiment faster, and even scale your solutions. The good thing about this is that you don’t need to learn everything at once. Start with Python libraries and gradually move toward advanced frameworks and GenAI platforms.
Key tools to master in this step:
- Data Handling & ML: NumPy, Pandas for data manipulation, and Scikit-Learn for classical ML models.
- Deep Learning: TensorFlow is used for industry-scale, and PyTorch can be used for research & prototyping.
- GenAI / LLMs: Try practicing with pre-trained models like Hugging Face, LangChai, and OpenAI APIs.
- Visualization: Use Matplotlib, Seaborn (Python plots), Tableau/Power BI (business dashboards) for visualization.
Starter project idea:
- Use Pandas + Matplotlib to analyze and visualize a dataset like sales trends.
- Train a small deep learning model using TensorFlow/PyTorch.
- Deploy a Hugging Face sentiment analysis model.
These are just examples; you can always take up a more interesting project and practice your skills along with building your portfolio.
Step 4: Hands-on Projects
Building projects is what makes you credible in this skill. It helps you connect concepts with practice, and they also act as proof of skills when you showcase them on GitHub or in interviews. Start small with beginner projects, gradually increase complexity, and finally take on advanced, real-world challenges.
At Scaler, we emphasize projects at every stage, so by the time you finish, you’ll already have a portfolio, which becomes a great addition to your resume.
Project Roadmap in accordance with your skill level:
- Beginner: Start with simple models like a spam email classifier, a movie recommendation system, or a basic house price prediction model.
- Intermediate: Take on projects such as sentiment analysis on tweets, image recognition with CNNs, or a sales forecasting model.
- Advanced: Challenge yourself with real-world tasks like building a chatbot using LLMs, a fraud detection system, or an autonomous image captioning model.
You can use public datasets from Kaggle or UCI to practice, and always document your process; these projects will help recruiters understand your technical skills better.
Step 5: Specialize in an AI Domain
By now, you’ll have a solid foundation and some projects to show. The next step is to choose a specialization based on your interests and career goals.
AI is a vast field, and you don’t have to master everything. Instead, pick one domain where you’d like to go deeper and build expertise. This makes you stand out in the job market and also keeps your learning focused.
Choosing your specialization is extremely important, as this is what you will be working on. Hence, at Saler, our modules let you to explore areas like NLP, Computer Vision, and Generative AI, so you can align your learning with the roles you’re aiming for.
Step 6: Build Portfolio & Certifications
All your skills and projects require credible certifications, and those experiences have to be added to a portfolio.
A strong portfolio not only proves what you know but also demonstrates your ability to solve problems. This is what recruiters and hiring managers actually look for. Start by uploading your projects to GitHub, participating in Kaggle competitions, and writing short project summaries on LinkedIn or a personal blog. Over time, your portfolio becomes your biggest strength.
That’s why we at Scaler help learners create industry-ready portfolios by guiding them on real projects and encouraging GitHub contributions, so by the end of the program, you’ll have an interview-ready portfolio. Key ways to strengthen your profile:
- GitHub: Publish all projects with clean code, documentation, and results.
- Kaggle: Compete in challenges and share notebooks.
- Certifications: Validate your expertise with credentials. You can sign in to programs like the Saler AI/ML Program.
With this six-step roadmap, you have a clear path to move from beginner to advanced in AI. Start with the basics, gradually build core skills, get hands-on with tools, and apply your knowledge through projects.
As you specialize and build your portfolio, you’ll not only gain confidence but also stand out in the job market. The journey may feel challenging at times, but with consistent practice and the right guidance, mastering AI becomes an achievable goal.
How Long Does It Take to Learn AI?
The time it takes to learn AI depends on your starting point, how consistently you practice, and the depth you want to reach. Unlike some technical skills that can be mastered quickly, AI is a broad and evolving field. Hence, it requires steady learning and practice.
-
Beginner to Intermediate (6-9 months): If you dedicate about 10 hours per week, you can build a strong foundation in Python, mathematics, and core machine learning concepts within this timeframe. By the end of this phase, you should be able to work on small projects like a spam classifier or a recommendation system.
-
Intermediate - Advanced (1–2 years): Moving into advanced areas like deep learning, NLP, computer vision, and generative AI takes longer. This stage involves mastering frameworks like TensorFlow/PyTorch, working with large datasets, and building complex projects such as chatbots or fraud detection systems.
-
Ongoing Learning: Also, AI isn’t something you finish learning. Since new models and frameworks emerge rapidly, continuous upskilling is part of the journey. Even professionals with years of experience keep updating their skills to stay relevant.
The good news is you don’t have to figure it all out alone. Structured programs like Scaler’s AI/ML course are designed with realistic timelines and guided mentorship, so you progress step by step without losing direction.
Best Ways to Learn AI
You can try learning AI with various sources. The best approach is to combine learning through courses/programs with handling projects. Here are some proven ways to build both knowledge and experience:
Courses & Bootcamps
Structured programs give you a clear roadmap and mentorship, making it easier to progress without confusion. Platforms like Scaler, Coursera, edX, and DataCamp offer guided AI/ML courses that cover everything from beginner concepts to advanced specializations.
Also Read: What Students Wished They Knew Before Joining Scaler
Books & Reading
For learners who prefer an in-depth understanding, books are the best resource to take help from. Classics like “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” by Russell & Norvig cover the theory of AI, while “Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow focuses on modern neural networks. Reading alongside practice helps solidify concepts and deepen intuition.
AI Communities
Joining AI-focused groups on Reddit, Discord, or LinkedIn will help you connect with peers, mentors, and industry experts. Communities keep you updated on the latest trends, help you troubleshoot problems, and provide networking opportunities for career growth.
Also, as we have mentioned previously, try practicing with real-time projects; this will help you not only practice your skills but also build your portfolio.
Careers in AI
There are various career options once you are equipped with AI, each with distinct roles, responsibilities, and salary potential. Here's a quick look at some popular options: Data Scientist: Use data analysis, statistics, and machine learning to extract insights and help with business decisions.
Machine Learning Engineer: You can build and deploy ML models while transforming algorithms into real-world applications.
AI Research Scientist: If you have your interest at heart, to get into the subject, then you can definitely choose to be an AI researcher. Here, you will develop new models, publish research, and work further to push AI boundaries.
NLP Engineer: You can specialize in natural language, i.e, language modeling, text processing, and building conversational systems.
Computer Vision Engineer: Focus on enabling machines to interpret images and videos for applications like detection and classification.
AI Product Manager: You can work as a bridge between business analysis and data production. Here you will define product strategy, guide AI feature development, and lead cross-functional teams.
All these roles are based on the skills and experience you attain. Want to know how much they’d pay? Let’s check out!
Salary Range: India vs. Global
These salary ranges are based on current market standards; they are likely to change in the future:
| Role | India (Rupee) | Global (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Scientist | ₹8-30 LPA | $130K-140K |
| Machine Learning Engineer | ₹6-25 LPA | $150K-160K |
| NLP Engineer | ₹10-35 LPA | $120k+ |
| Computer Vision Engineer | ₹12-40 LPA | $168K (avg.) |
| AI Research Scientist | ₹15-50 LPA | Entry-level: 100K+, Senior: 200K+ |
| AI Product Manager | ₹40-70 LPA | $128K avg. |
Conclusion
Learning AI may seem like a long journey, but with the right approach, it becomes both manageable and rewarding.
Start with the prerequisites: math, programming, and data handling. Then, move on to building strong skills in machine learning, deep learning, NLP, and computer vision.
Once the basics are in place, practice with tools and frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face. Practical projects are the next step, helping you apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Finally, choose a specialization that aligns with your career goals, whether that’s NLP, computer vision, robotics, or generative AI.
Remember, in AI, consistency matters more than speed. Even a few hours every week, if spent regularly, can compound into significant progress over time. If you’re looking for structured guidance, consider exploring Scaler’s AI/ML programs, designed to take learners from basics to industry readiness with mentorship and projects.
Have any more doubts? Check out the FAQ Section:
FAQs
Can I learn AI without coding?
Yes, you can start with low-code or no-code platforms like Google AutoML, Runway, or ChatGPT APIs. However, to grow into advanced roles, learning coding, especially Python, is highly recommended.
Is AI difficult to learn?
AI feels overwhelming at first, but with a well-rounded roadmap, starting from math basics to projects, you can progress steadily. Consistency matters more than prior expertise.
Can non-tech people learn AI?
Yes. Many learners from business, design, or finance backgrounds have transitioned into AI. Start with beginner-friendly tools and courses, then gradually build technical depth.
Which AI tools are best for beginners?
For starters, Python libraries like Pandas and Scikit-Learn are great. If you want quick, practical experience, try Hugging Face, which is a pre-trained model, or Google Colab for free practice.
Do I need a degree for AI jobs?
Not always. While computer science or engineering degrees help, many companies now hire based on skills, projects, and certifications. A solid GitHub portfolio and Kaggle participation can weigh as much as a degree.
Can I get a job in AI in under 1 year?
Yes, entry-level roles like Data Analyst, ML Intern, or AI Associate are possible within 6-12 months if you commit 10-15 hours weekly, focus on projects, and showcase your work.
