Schema in DBMS
Overview
Schema in DBMS describes how the data should be organized and it also represents the logical constraints that are applied to the data. Schema represents the structure of the database and it helps the programmer to understand the database.
The data which is present in the database at a particular time is known as Instance in DBMS.
Introduction
Database Schema is a Logical Representation of the Database. Now, what do I mean by logical representation?
Let’s understand this by the below example:
When the data is stored in the database, its physical representation is different. Like data is stored in form of files. But Logical Representation is the skeleton of the database.
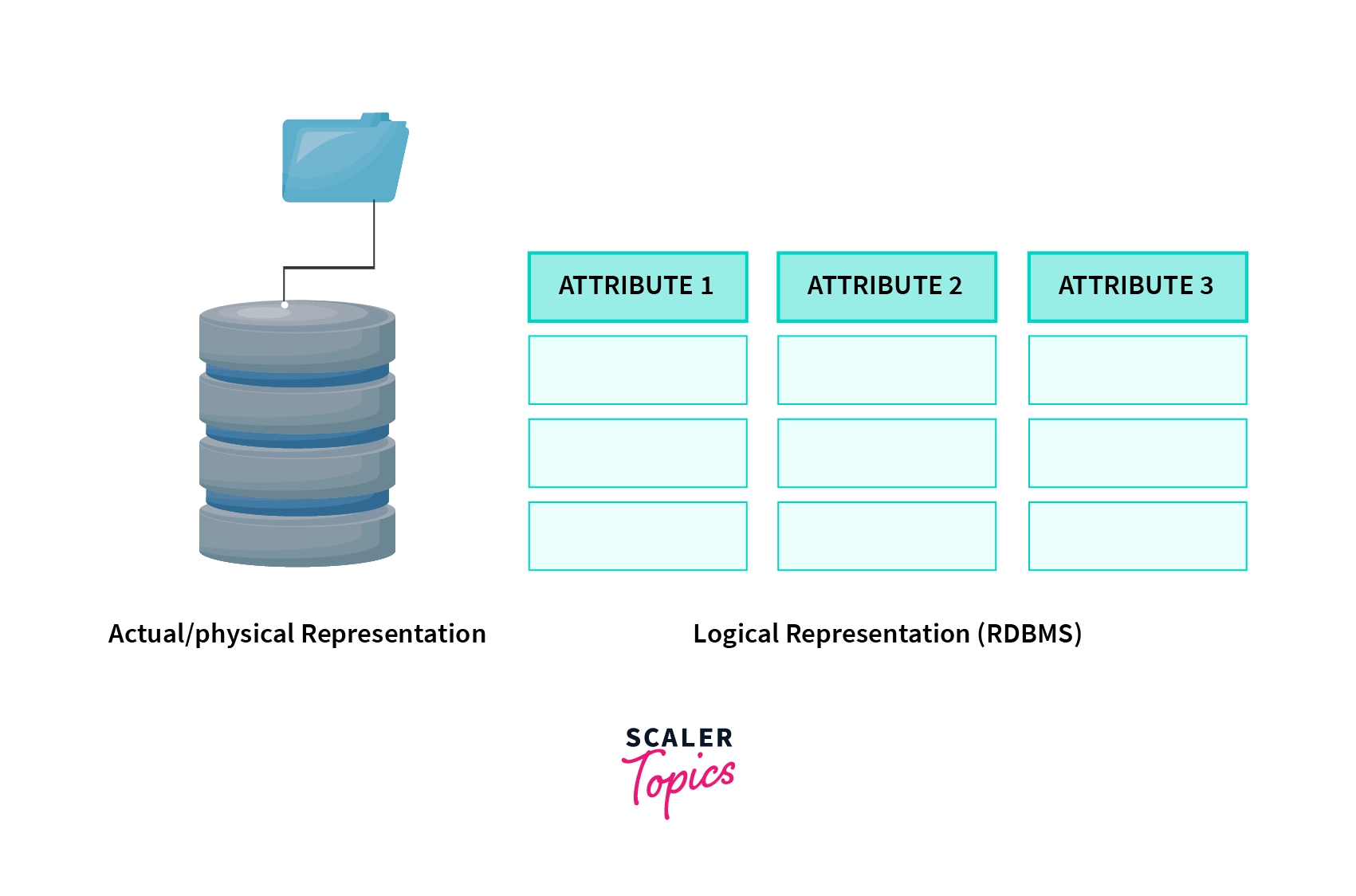
In the case of RDBMS(Relational Database Management System), Data is logically represented in form of tables/relations. Similarly, in the case of the E-R Model, Data is logically represented in form of entities and relationships.
For Example, if we would like to store a student's detail, hence we will need a STUDENT table consisting of attributes such as roll number, name, course, etc.
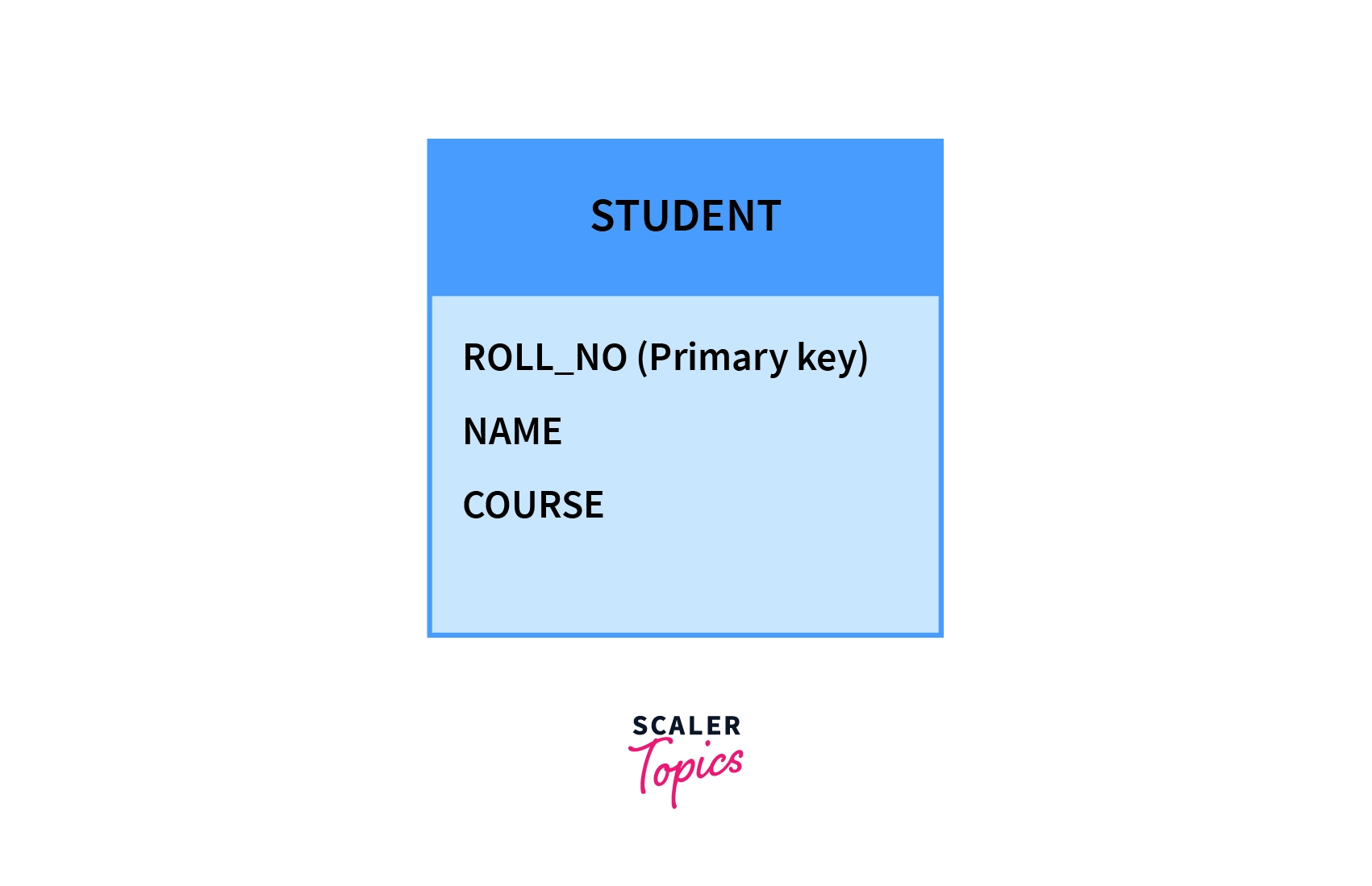
The above Schema will be rendered as:
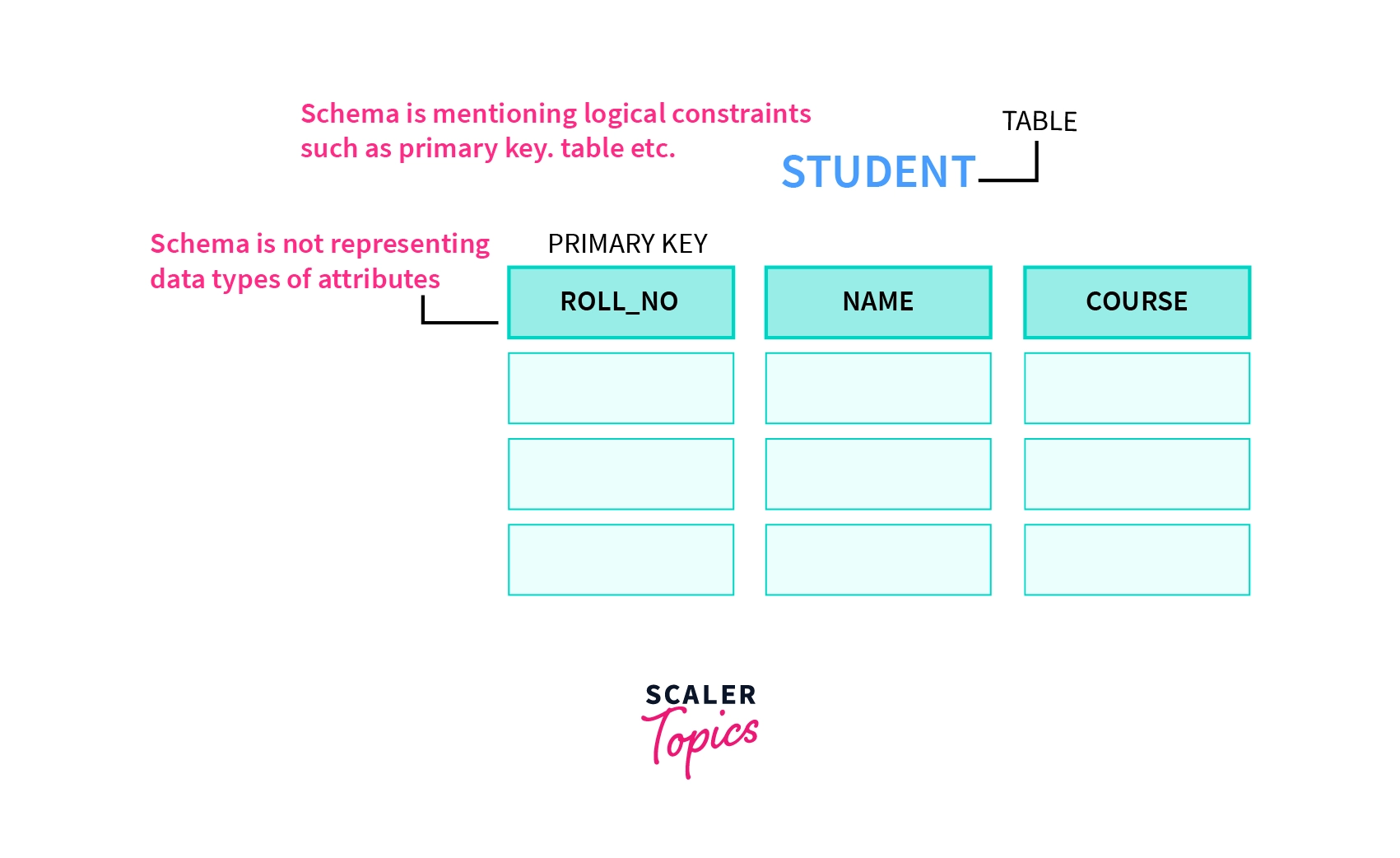
What is Schema in DBMS?
As you can see, these attributes create a structure/skeleton of the database and this structure is known as "schema".
Here, schema doesn't represent the constraints of the database such as data type used in the attributes. But it contains logical constraints such as Table, Primary Key, etc.
To break the direct contact between the user and the database.
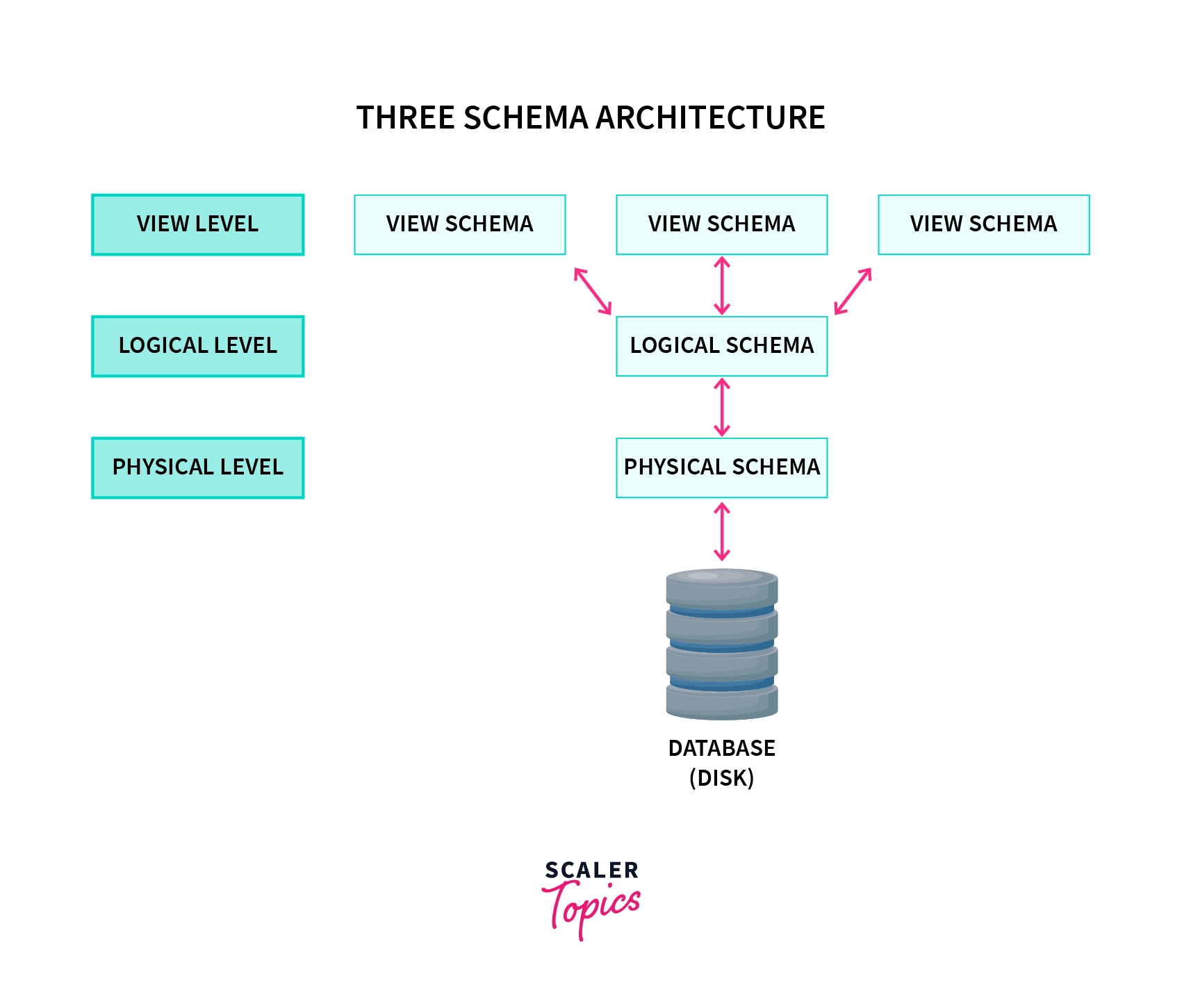
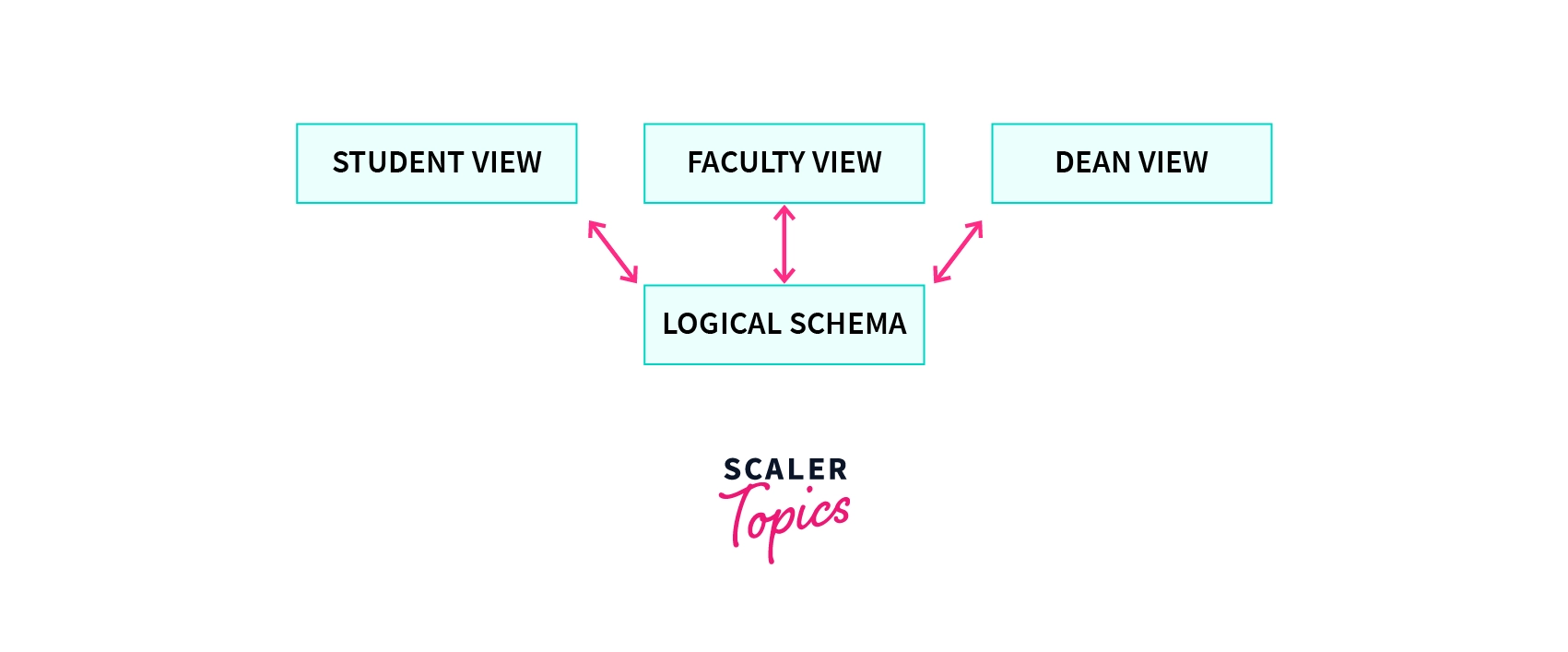
Three Schema Architecture was introduced in 1970 and it consists of three levels: View, Logical, and Physical Level.
Three Schema Architecture
Physical Schema in DBMS
Physical Schema describes where the data is actually/physically present.
Here, the Database administrator decides where should be the data stored and how it should be stored in different blocks of storage.
Logical Schema in DBMS
Logical Schema or also known as Conceptual Schema represents the structure of the database.
So for a student database, it describes the attributes/columns of the table. As discussed above, it also describes the logical constraints.
View Schema in DBMS
View Schema or also known as External Schema is how the data is presented to a user.
Let's understand this with an example:
For a university's student management system, when a student logins into the system, the system shows Student details such as name, roll number, marks, department, year, etc.
These end-interactions with the database are described by View Schema in DBMS.
Screen showing details of a student
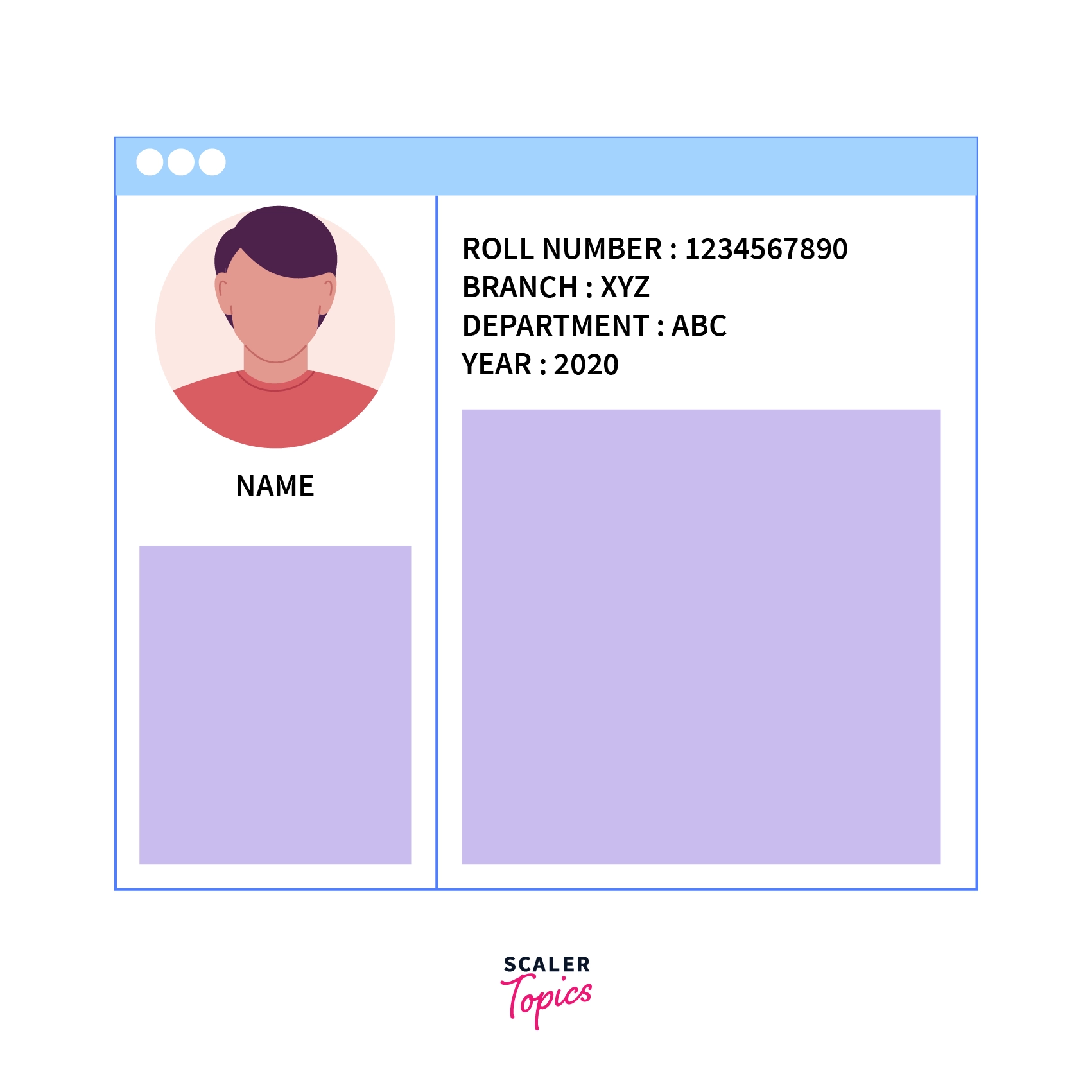
But, Will this view be the same for every student?
Obviously not, that's why there are multiple View Schemas in View Level.
Different View Schmeas
Creating Schema in DBMS
Creating a database schema in a DBMS (Database Management System) involves designing the structure of the database by defining the tables, their attributes, and the relationships between them. A schema is essentially a blueprint of the database that defines its logical structure, constraints, and integrity rules. It provides a framework for organizing and storing data in a consistent and efficient manner.
The schema creation process involves creating tables and defining their columns and data types. Each table represents a unique entity or concept in the database, such as customers, orders, or products. The attributes of each table define the characteristics of the data stored in them, such as the name, age, address, and other relevant details.
In addition to defining the tables and attributes, the schema also includes the relationships between the tables. These relationships define how the tables are connected and how data is shared between them. For example, a customer may place multiple orders, so there would be a relationship between the customer and order tables.
Creating a schema involves careful planning and consideration of the data that will be stored in the database. It should be designed in a way that ensures data consistency, accuracy, and completeness while optimizing the performance of the database. Once the schema is created, it provides a foundation for data storage and retrieval, and any changes to the schema should be carefully managed to ensure the integrity of the database is maintained.
Schema Designs
Database Schema design involves creating a database schema that defines the structure of the database and the relationships between the tables. A well-designed schema is critical to the performance, flexibility, and scalability of a database.
There are several principles that guide schema design, including normalization, denormalization, and indexing. Normalization is the process of breaking down tables into smaller, more manageable pieces, to reduce redundancy and improve efficiency. Denormalization involves combining tables to improve query performance, at the cost of some data redundancy. Indexing is the process of adding indexes to tables to improve query performance.
Effective schema design also involves considering factors such as data access patterns, query complexity, and scalability requirements. For example, a schema designed for a transactional system may differ significantly from one designed for an analytical system.
Schema design should be an iterative process, involving testing and refinement to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. It should also be flexible enough to accommodate future changes in data requirements or technology advancements.
In summary, schema design is a critical aspect of database development, and a well-designed schema can significantly improve the performance, flexibility, and scalability of a database.
DBMS Instance
Database Schema is designed before creating the database and once the database is functional it is very difficult to update the schema as it represents the core structure of the database. Also Schema doesn't represent any data/information stored in the database.
In a database, there will be many read, and write operations. So we can't say we have content in the database as the data in the database is changing frequently.
So Instance in DBMS represents the data/information present in the database at a particular instance/time.
Let's say we have a STUDENT table, below is the representation of the table on 16th May.
Suppose a new student is enrolled in the university on 17th May. Now the database will be updated and this is shown below.
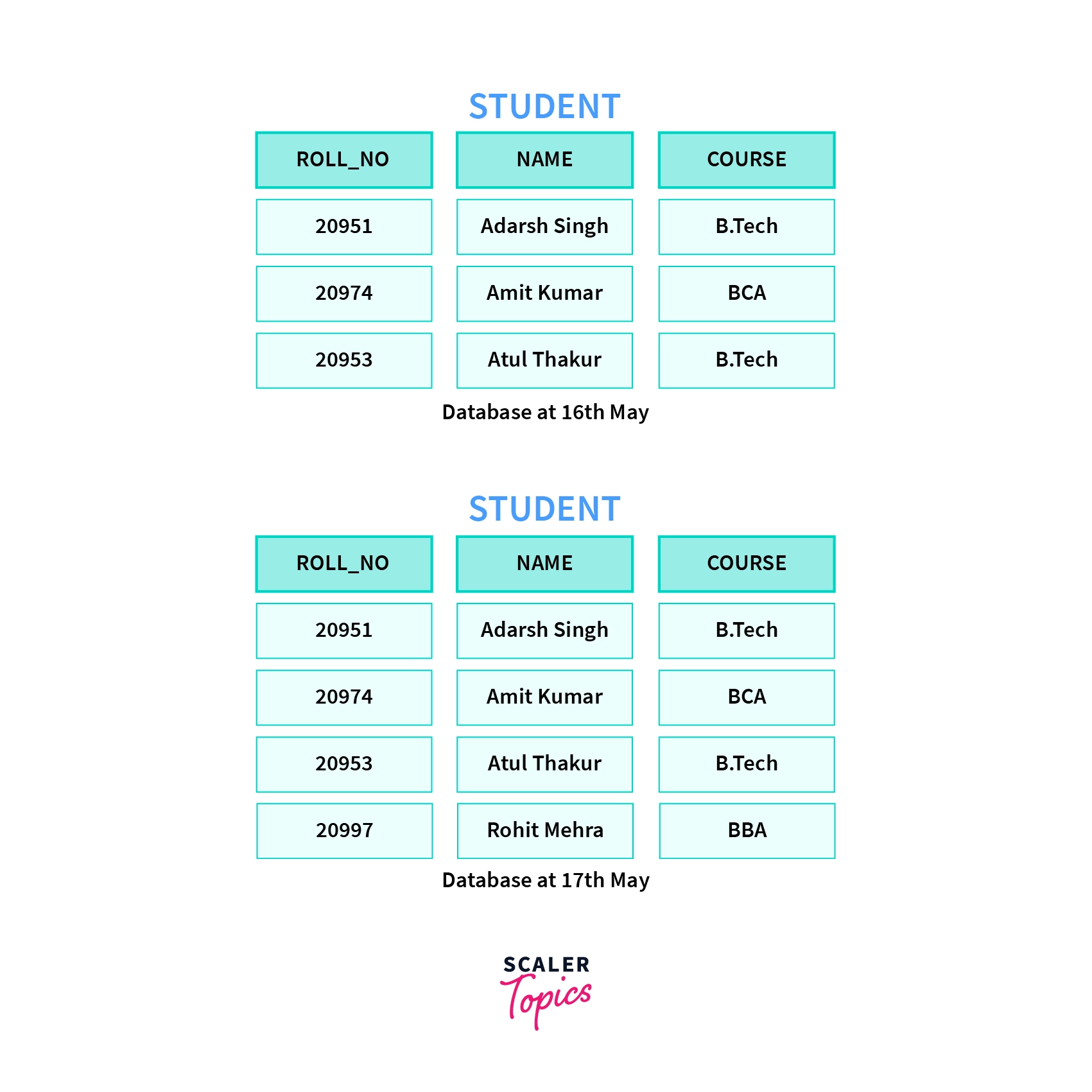
Now, if we say we need instance of STUDENT table on 16th May, Table present at the left will be returned.
But, when we say we need instance of STUDENT table on 17th May, Table present on the right will be returned.
Conclusion
- The Schema is the Structure of the database and it represents logical constraints such as Table, key, etc.
- To break direct contact between the user and the database, Three Schema Architecture was introduced and it consists of three levels: View, Logical and Physical Level.
- Since data stored in the database is changing frequently, Instance represents the data present in the database at a particular time.

