What is Segregation of Duties (SoD)?
Segregation of duties (SoD) is a key concept in cybersecurity and is concerned with ensuring that no single individual has complete control over a particular process or function. The purpose of Segregation of Duties (SoD) is to prevent fraud, errors, and other malicious activities by spreading the responsibility for a process or function across multiple individuals.
In the context of cybersecurity, Segregation of Duties (SoD) is typically applied to areas such as access control, user management, incident response, and data backup and recovery. For example, an organization might assign one individual to manage user accounts, another to monitor network activity, and another to perform backups. This ensures that no one individual can both create a user account and modify the permissions assigned to that account.

Segregation of Duties (SoD) is an important control for organizations of all sizes, as it helps to reduce the risk of internal fraud, cyber-attacks, and other malicious activities. This is because it provides multiple layers of defense against such activities, and helps to ensure that even if one individual is compromised, other controls are in place to detect and prevent the malicious activity from proceeding.
To implement Segregation of Duties (SoD) effectively, organizations must carefully assess their business processes and identify areas where a risk of fraud or malicious activity exists. This may involve conducting a risk assessment, mapping out business processes, and identifying critical functions and processes that require multiple layers of oversight and control.
Need for Segregation of Duties
In the context of cybersecurity,` Segregation of Duties (SoD) refers to the practice of spreading the responsibility for a process or function across multiple individuals so that no single person has complete control over it.
Cyber threats are constantly `evolving, and organizations face an increased risk of data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other malicious activities. In many cases, these threats originate from insiders, such as employees, contractors, or third-party vendors, who have access to sensitive information and systems.
This is where the need for Segregation of Duties (SoD) in cybersecurity becomes apparent. By dividing critical tasks into smaller components and assigning those components to different individuals, organizations can minimize the risk of malicious activities and ensure that multiple layers of defense are in place.
For example, an organization might assign one individual to manage user accounts, another to monitor network activity, and another to perform backups. This ensures that no one individual can both create a user account and modify the permissions assigned to that account, reducing the risk of a malicious insider misusing their access.
In addition to reducing the risk of malicious activities, Segregation of Duties (SoD) also helps organizations improve accountability and comply with regulations and industry standards. For example, many regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), require organizations to have Segregation of Duties (SoD) controls in place to ensure the security of sensitive information.
Concepts in Segregation of Duties
Segregation of duties is implemented based on two important concepts: Segregation of Duties (SoD) conflicts and Segregation of Duties (SoD) violations
- Segregation of Duties (SoD) Conflicts: Segregation of Duties (SoD) conflicts arise when the implementation of Segregation of Duties (SoD) controls makes it difficult or impossible for individuals to perform their duties effectively.
For example, in a scenario where an individual responsible for access control does not have the necessary permissions to modify the access controls for a specific user account, this can create a conflict between the need for security and the need for functionality. The individual is unable to perform their duties effectively, but granting them the necessary permissions would undermine the security controls in place.
Another example of an SoD conflict in cybersecurity could be when the implementation of `SoD controls restricts access to sensitive information to a single individual, making it difficult for others to perform their duties effectively. For example, if an individual responsible for security incident response does not have access to critical systems or information, they may not be able to respond to security incidents effectively.
Segregation of Duties (SoD) conflicts can have significant consequences for organizations, including decreased efficiency, increased risk of cyber attacks, data breaches, and other malicious activities, and decreased overall security. Organizations must be proactive in addressing SoD conflicts and finding solutions that balance the need for security and functionality.
This may involve reviewing So) controls and processes, assessing the risks associated with the Segregation of Duties conflicts, and implementing controls to prevent and detect SoD conflicts.
For example, organizations might implement regular audits and monitoring of critical systems and processes to detect SoD conflicts, as well as implement user training programs to educate individuals on the importance of Segregation of Duties and the consequences of Segregation of Duties conflicts.
In conclusion, conflicts are an important aspect of the Segregation of Duties in the context of cybersecurity that organizations must be aware of and address. By implementing effective Segregation of Duties controls and addressing SoD conflicts, organizations can minimize the risk of cyber attacks, data breaches, and other malicious activities, and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information is protected.
- Segregation of Duties (SoD) Violations: Segregation of Duties (Segregation of Duties (SoD)) violations are a critical concern in the context of cybersecurity. A Segregation of Duties (SoD) violation occurs when individuals bypass or circumvent SoD controls and perform tasks that they are not authorized to perform. In the context of cybersecurity, SoD violations can lead to significant security risks, including data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and other malicious activities.
For example, a Segregation of Duties (SoD) violation in the context of cybersecurity might occur when an individual responsible for managing user accounts creates a new user account for themselves with elevated privileges. This could allow the individual to access sensitive information or systems that they are not authorized to access, potentially leading to a data breach or other malicious activity.
Another example of SoD violation could be when an individual bypasses security controls and accesses sensitive information without proper authorization. For example, an individual with access to sensitive information might email the information to an unauthorized third party, or transfer the information to a removable storage device.
SoD violations can have significant consequences for organizations, including decreased efficiency, increased risk of cyber attacks, data breaches, and other malicious activities, and decreased overall security. Organizations must be proactive in addressing SoD violations and finding solutions that balance the need for security and functionality.
This may involve reviewing `Segregation of Duties (SoD) controls and processes, assessing the risks associated with SoD violations, and implementing controls to prevent and detect SoD violations. Organizations might implement regular audits and monitoring of critical systems and processes to detect SoD violations, as well as implement user training programs to educate individuals on the importance of Segregation of Duties and the consequences of SoD violations. In conclusion, SoD violations are a critical concern in the context of cybersecurity that organizations must be aware of and address.
Some Examples of Segregation of Duties Applications
Here are some examples of the application of Segregation of Duties (SoD) in the context of cyber security:
- Access Control: Segregation of Duties (SoD) can be used to ensure that different individuals are responsible for different aspects of access control. For example, one individual might be responsible for managing user accounts and granting access privileges, while another individual is responsible for monitoring access logs and detecting unauthorized access attempts.
- Incident Response: In the context of incident response, Segregation of Duties (SoD) can be used to ensure that different individuals are responsible for different aspects of incident response. For example, one individual might be responsible for identifying security incidents, while another individual is responsible for investigating the incident and taking appropriate remedial actions.
- Network Security: In the context of network security, Segregation of Duties (SoD) can be used to ensure that different individuals are responsible for different aspects of network security. For example, one individual might be responsible for configuring firewalls and other network security devices, while another individual is responsible for monitoring network activity and detecting potential security threats.
- Data Protection: In the context of data protection, Segregation of Duties (SoD) can be used to ensure that different individuals are responsible for different aspects of data protection. For example, one individual might be responsible for managing access to sensitive data, while another individual is responsible for encrypting and backing up data to ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
How to Implement Segregation of Duties?
Implementing Segregation of Duties (SoD) in the context of cyber security requires a comprehensive approach that involves understanding the risks associated with SoD violations, assessing the critical processes and functions in an organization, and designing and implementing effective SoD controls. Here are the steps organizations can follow to implement SoD in the context of cyber security:
- Assess Risks: The first step in implementing SoD is to assess the risks associated with SoD violations in the context of cyber security. This involves identifying the critical processes and functions in the organization and assessing the potential impact of SoD violations on those processes and functions.
- Identify Critical Processes and Functions: Once the risks have been assessed, the next step is to identify the critical processes and functions in the organization. This involves determining which processes and functions are critical to the organization's operations and which processes and functions are critical to the security of sensitive information.
- Divide Processes and Functions: The next step is to divide the critical processes and functions into smaller components and assign those components to different individuals. This ensures that no single person has complete control over a process or function, reducing the risk of SoD violations.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Once the critical processes and functions have been divided, the next step is to assign roles and responsibilities to individuals. This involves determining which individuals are responsible for which components of critical processes and functions, ensuring that individuals are only able to perform the tasks for which they are authorized.
- Implement Access Controls: The next step is to implement access controls to prevent unauthorized access to critical systems and data. This involves implementing controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Monitor Processes and Functions: The final step is to monitor processes and functions to detect SoD violations and ensure that SoD controls are functioning as intended. This involves monitoring access logs and system activity to detect potential SoD violations, and conducting regular audits of critical systems and processes to ensure that SoD controls are functioning as intended.
Best Practices for Segregation of Duties Security
Here are some best practices for implementing SoD in the context of cyber security:
-
Regularly Review and Update SoD Controls: Regularly review and update SoD controls to ensure that they are effective and appropriate for the organization's changing needs. This involves reviewing` SoD controls at least annually and updating them as necessary to reflect changes in the organization's processes and functions.
-
Train Employees: Train employees on the importance of SoD and the procedures they must follow to ensure that SoD controls are functioning as intended. This involves providing regular training and education to employees on the importance of SoD and the procedures they must follow to ensure that SoD controls are functioning as intended.
-
Create an SoD Risk Matrix: Enlist all the duties, and identify individuals who are responsible for performing each duty to identify any SoD conflicts. One of the most important prerequisites to creating an SoD matrix` is to understand what each duty means and what are the underlying risks. Analyse which tasks are easy to perform by the same role and which tasks must be separated to ensure security.
-
Risk management and assessment: Once the risks have been assessed, the next step is to identify the critical processes and functions in the organization. Risk assessment should be repeated after regular intervals and after some major changes in the organization. This is a dynamic process. This involves determining which processes and functions are critical to the organization's operations and which processes and functions are critical to the security of sensitive information.
Need for Creating a SOD Matrix
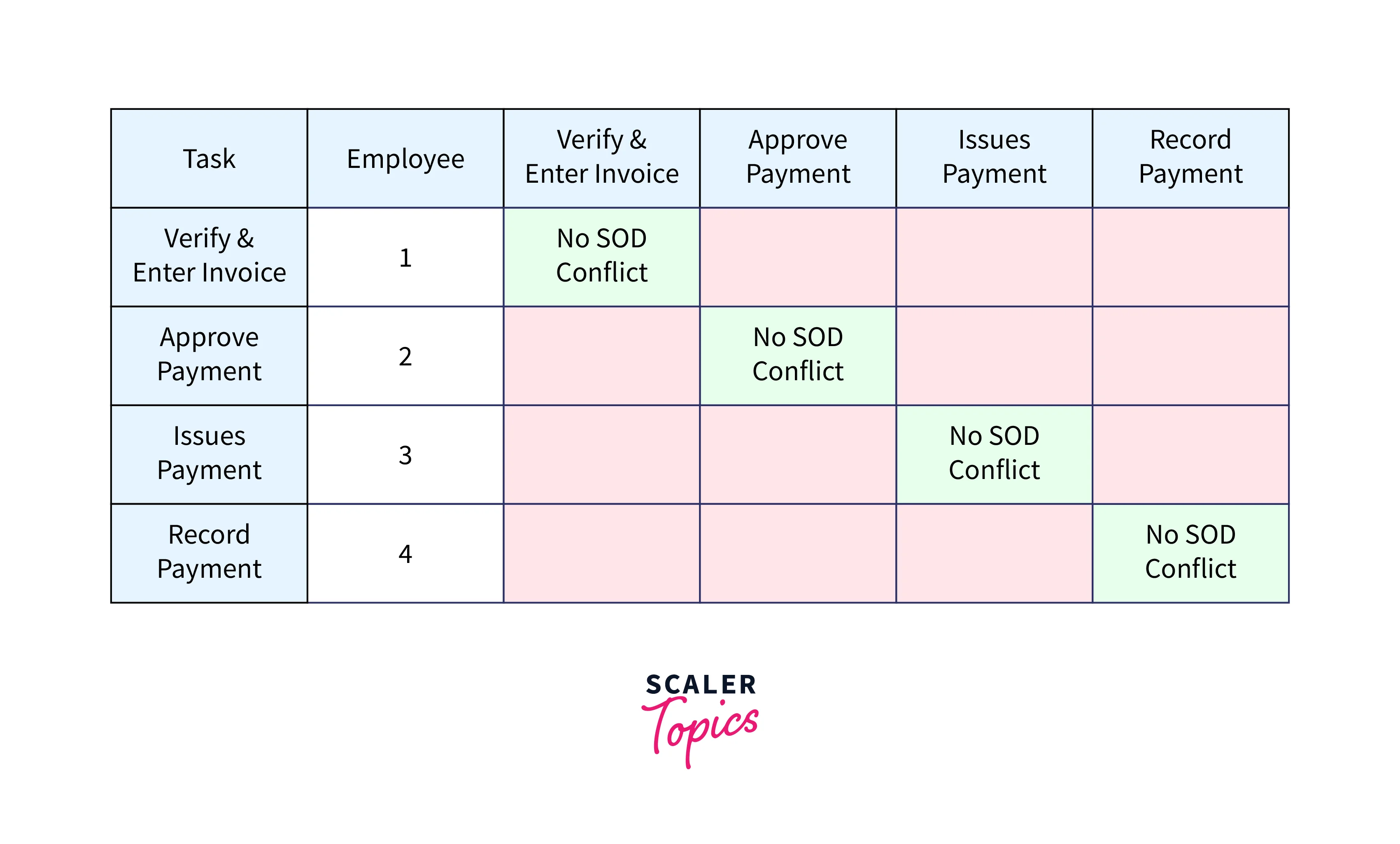
A Separation of Duties (SoD) matrix is a crucial component of any cyber security program, as it helps ensure that no single individual has complete control over a sensitive process or system. The main purpose of creating an SoD matrix is to minimize the risk of fraud, errors, or malicious actions by enforcing accountability and reducing the potential for a single point of failure.
In a typical organizational setting, employees perform a variety of tasks and have access to various systems and data. However, granting complete control to an individual for multiple critical functions increases the risk of potential problems such as theft, fraud, errors, or other malicious activities. In such scenarios, the organization may have a difficult time detecting the source of the problem, making it difficult to rectify the situation. This is where an SoD matrix comes into play, as it helps to distribute the control over critical processes and systems among different individuals, thus reducing the risk of a single point of failure.
An SoD matrix is essentially a matrix of users, roles, and responsibilities that outlines the tasks that each individual is authorized to perform. The matrix provides a clear definition of the roles and responsibilities of each individual and the systems and processes to which they have access. The matrix can be used to track access privileges and changes to those privileges over time, making it an important tool for auditing and monitoring the security of systems and processes.
For example, in a financial institution, an SoD matrix can help to ensure that the person who processes transactions is not the same person who has access to the accounts being transacted. This helps to minimize the risk of fraud and ensures that there is a clear trail of evidence in the event of any fraudulent activities.
An SoD matrix can also be used to enforce compliance with regulations and policies, such as data privacy regulations and internal security policies. This is especially important in highly regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and government, where strict controls over access to sensitive information are required.
When creating an SoD matrix, it is important to consider the risk of each system and process and determine which tasks should be separated. For example, tasks that involve the handling of sensitive information or critical processes should be separated from less critical tasks. Additionally, it is important to consider the interdependencies of different systems and processes and ensure that the SoD matrix takes these interdependencies into account.
Learn More
Scaler maintains a series of blogs on cyber security. Feel free to learn more at scaler topics
Conclusion
-
Segregation of duties is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity as it helps to prevent fraud and ensure accountability in the handling of sensitive information and systems.
-
By dividing the responsibility for different security-related tasks among different individuals, segregation of duties helps to minimize the risk of a single point of failure.
-
When implemented properly, segregation of duties helps to maintain a balance between efficiency and security, allowing organizations to protect their assets while still being able to effectively operate.
-
Regularly reviewing and updating the segregation of duties policies and procedures can help to ensure that they remain effective in the face of changing threats and technology.
-
Ultimately, effective segregation of duties is a critical component of a comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity strategy, helping `organizations to minimize the risks associated with the handling of sensitive information and systems.
