Sort a Linked List

Overview
A linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links. The data element of a linked list is known as a node which contains two parts namely- the data part and the pointer. For sorting a linked list, we can use the insertion sort-based algorithm as well as the merge sort algorithm. The insertion sort-based algorithm uses nested loops so its time complexity comes out to be higher than the merge sort algorithm. The merge sort algorithm simply divides the list into smaller halves and then sorts the smaller ones. Finally, the smaller ones are merged in a sorted fashion to get the complete sorted list.
Takeaways
- Time complexity for sorting linked list using merge-sort:
What is Linked List?
As the name suggests, a linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links. The data element of a linked list is known as a node which contains two parts namely- the data part and the pointer. The data part contains the actual data and the pointer part contains a pointer that points to the next element of the linked list.
There are various types of linked lists:
- Singly-linked list.
- Doubly linked list.
- Circular linked list.
- Doubly circular linked list.
- Skip linked list, etc.
To learn more about Linked Lists, refer here.
Concept of Sorting Linked List
For sorting a linked list, we can use an insertion sort kind of technique. We can use two points (let's say current and nextNode are those two pointers). At first, the current pointer will be to the head of the linked list and the nextNode pointer will point to the second node of the linked list (or the next node to the current node).
Now, we would traverse the entire linked list (until the current node is not equal to null), and in each step, we will check if the current node's data is greater than a node's data. In case it is larger, we will swap the data between them.
In each iteration, we will select one current node and place the currently selected node at its correct sorted position in the given linked list.
Example:
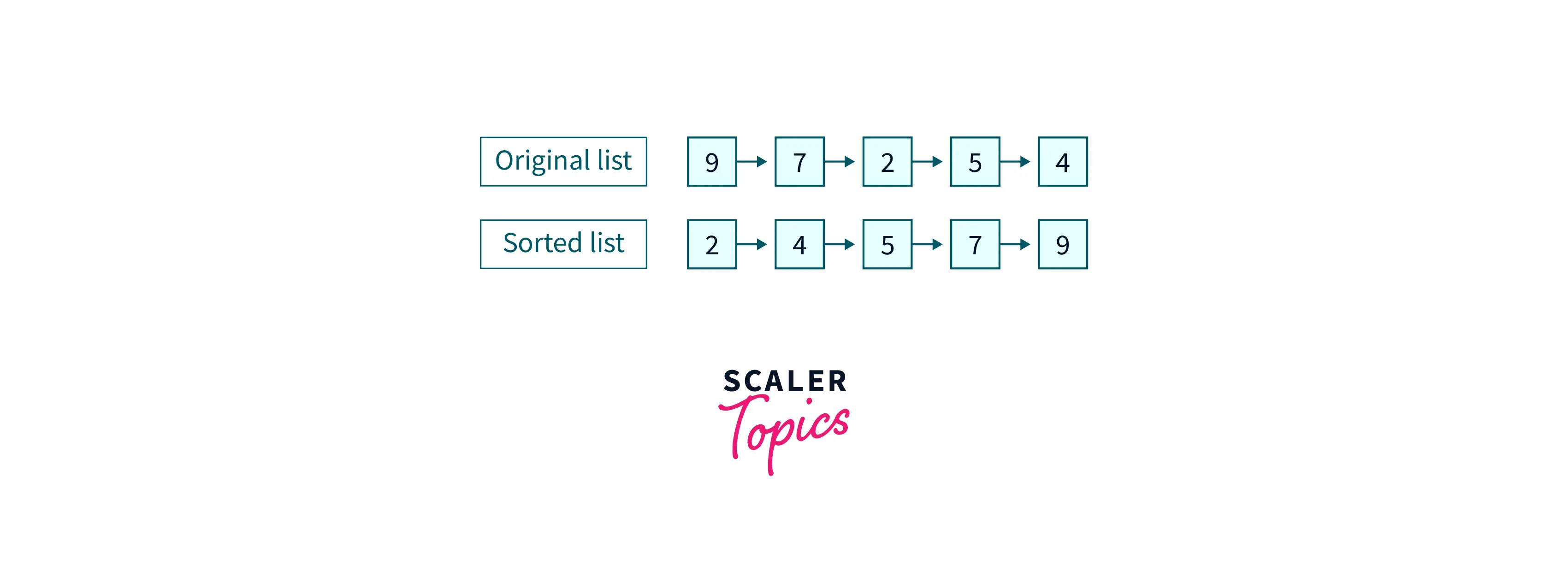
Refer to the algorithm and implementation of how we can sort a linked list for better understanding.
Algorithm to Sort Linked List
We need to call the sortLinkedList() function. Inside the sortLinkedList() function, we need to perform certain steps:
- We will first create two nodes namely current and nextNode .
- The current node will be pointing at the head of the linked list.
- The nextNode will be pointing to the second node of the linked list.
- In the next step, we need to compare all the nodes of the linked list with the current node. If the data of the current node is greater, then we need to swap the data of the current node and the the currently processing node.
- After the swapping, the current node will point to the next node to the current node (i.e. current->next).
- We will continue the entire above steps until the linked list is sorted.
Let us now try to code out the algorithm.
Program to Sort Linked List
Let us now look at the implementation of the algorithm to sort a linked list for more clarity.
C++ Code:
Java Code:
Python Code:
Output:
How to Sort a Linked List Using Merge Sort?
We can sort a linked list using the merge sort algorithm as well. Merge sort is one of the divide and conquer techniques as it divides the linked list into halves until the size of the linked list is greater than equal to one.
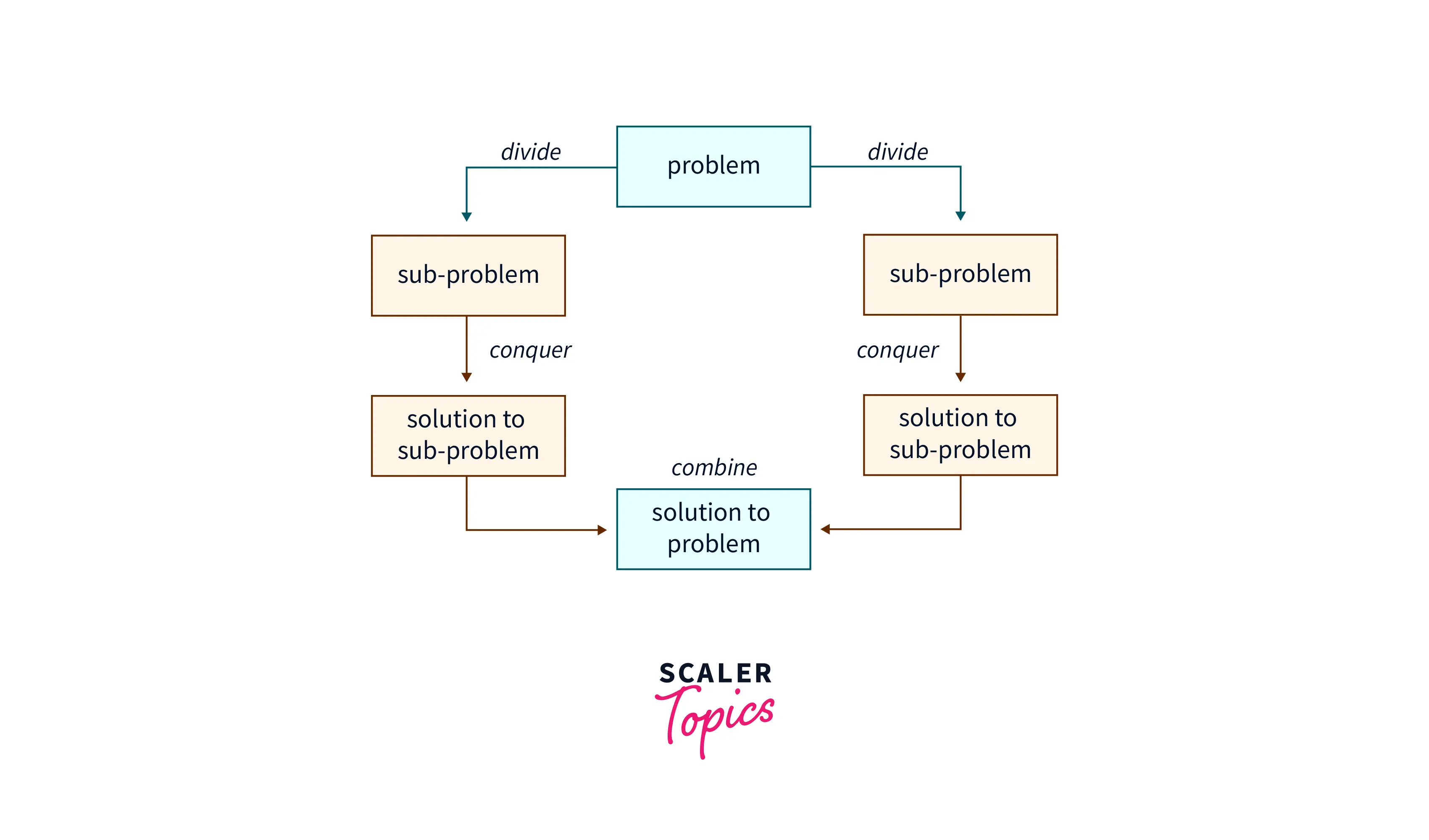
The idea of divide and conquer is very simple, just divide the input into smaller sub-problems and then find the solution to those smaller problems. Once the smaller problem is solved then the results can be combined to get the solution to a larger problem.
Refer to the diagram of the divide and conquer technique for better understanding.
The idea or merge sort is very simple, we will take an input linked list (let's say l), and we will divide it into halves until the size of the linked list is greater than equal to one. This step is known as the divide step.
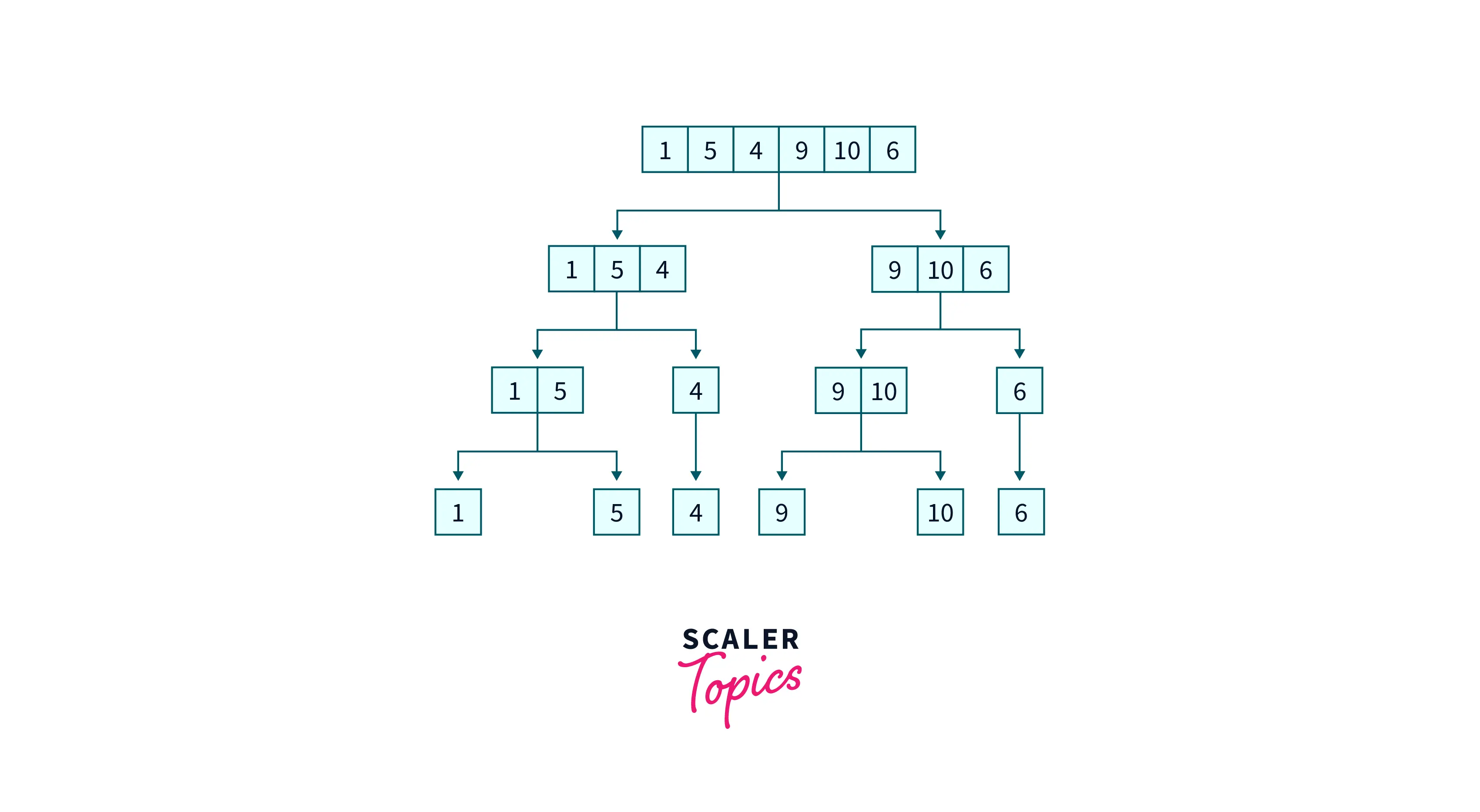
Suppose the input linked list is [1, 5, 4, 9, 10, 6]. Now in each step, we will divide it into halves as sorting the smaller portion is easier than sorting the entire linked list. Refer to the diagram specified below to understand how the division operation is taking place.
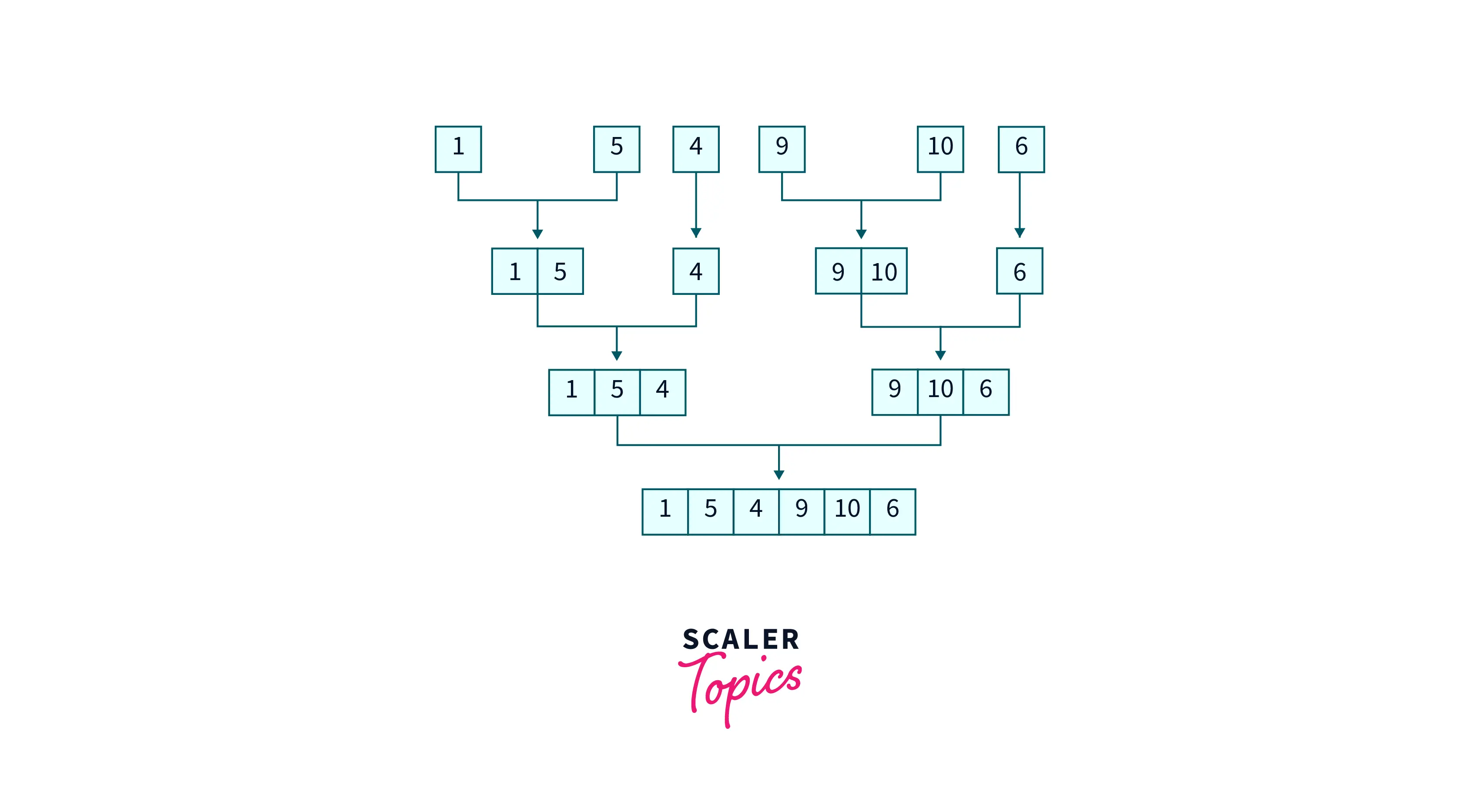
Now, in the conquer part, we will sort the smaller halves and then merge the sorted parts to get larger sorted portions. In this way, we will merge smaller sorted links in sorted order.
Refer to the diagram specified below to understand how the conquer operation occurs.
Let us now discuss the step-by-step algorithm.
Algorithm
We need to call the mergeSort() function. Inside the mergeSort() function, we need to perform certain steps:
- First, handle the base case i.e. if the head pointer of the linked list is pointing to null then we cannot perform anything, so return.
- Else, we will divide the linked list into smaller halves.
- Now, we will sort the smaller halves of the linked list.
- Finally, we will merge this sorted linked list and update the head pointer pointing to the head of the merged linked list.
Implementation
Let us now code the above-discussed algorithm for more clarity.
C++ Code:
Java Code:
Python Code:
Output:
Complexity
In the above approach, we are dividing the linked list into smaller halves and then perform some operations on it. We are also using an extra list or array in the merge operation to store the current result.
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the merge sort approach to sort a linked list comes out to be , where n is several nodes in a linked list.
For more detail about the calculation of the time complexity of this divide and conquer technique, refer here.
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the merge sort approach to sort a linked list comes out to be , where n is the size of the extra array or list used in the mere function.
Rearrange Linked List in Increasing Order
We have already discussed how we can sort a linked list, now arranging a linked list in increasing order is sorting a linked list. So, we will only see the sorting function that will sort the linked list or rearrange the linked list in increasing order.
Code
Let us now look at the implementation of the algorithm that we discussed previously. We will need pointers and a nested loop to arrange the linked list in increasing order.
C++ Code:
Java Code:
Python Code:
Complexity
In the algorithm to sort a linked list, we are traversing the linked list twice. In the traversal, we are only using two extra nodes.
Time Complexity
So, the time complexity of the algorithm to sort a linked list comes out to be , where n is the number of nodes in a linked list.
Space Complexity
Since we are not using any extra space in the linked list traversal, the space complexity of the algorithm to sort a linked list comes out to be .
Conclusion
- A linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links.
- The data element of a linked list is known as a node that contains two parts namely- the data part and the pointer. The pointer points to the next node of the linked list.
- For sorting a linked list, we can use the insertion sort type algorithm. In each iteration, one element of the linked list is moved to its correct position.
- The time complexity of the algorithm to sort a linked list comes out to be , where n is the number of nodes in a linked list. On the other hand, the space complexity of the algorithm to sort a linked list comes out to be .
- We can sort a linked list using the merge sort. Merge sort is one of the divides and conquer techniques as it divides the linked list into halves until the size of the linked list is greater than equal to one.
- The idea of divide and conquer is to divide the input into smaller problems and then find the solution to those smaller problems. Once the smaller problem is solved then the results can be combined to get the solution to a larger problem.
- In the merge sort approach to sort a linked list, we are dividing the linked list into smaller halves and then performing some operations on it. We are also using an extra list or array in the merge operation to store the current result.
- The time complexity of the merge sort approach to sort a linked list comes out to be , where n is the number of nodes in a linked list. On the other hand, the space complexity comes out to be .
