Data Models in DBMS

Overview
Nowadays, all enterprises require properly defined and formatted data to bring all the segments of an enterprise - IT, Management, and others together. Data models play a key role in solving this problem as they represent an enterprise's data and connections between them in a pictorial form.Without a defined data model, there is a risk of data inconsistency and redundancy, which can lead to poor data quality.
Before diving deeper, it is important to understand the basic concepts of data models. These basic concepts help establish a shared vocabulary and define the scope for all stakeholders involved.
In this article, we will be learning about data models in a types of data models in DBMS , and their advantages and disadvantages
What are Data Models in DBMS?
A data model helps organize, define, and access data within a DBMS by providing a clear structure that acts as a blueprint for efficient data management. Data models in DBMS help to understand the design at the conceptual, physical, and logical levels as it provides a clear picture of the data making it easier for developers to create a physical database.
Data models are used to describe how the data is stored, accessed, and updated in a DBMS. A set of symbols and text is used to represent them so that all the members of an organization can understand how the data is organized. A data model organizes data into structured formats, such as hierarchical or network models, visually and logically grouping related data to efficiently manage complex relationships. It provides a set of conceptual tools that are vastly used to represent the description of data.
There are many types of data models that are used in the industry. At the conceptual level, a conceptual data model is a high-level, abstract representation that captures business requirements, key entities, and relationships without technical details, making it useful for stakeholder communication.
Types of Data Models in DBMS
Hierarchical Model
The hierarchical data model is one of the oldest data models, developed in the 1950s by IBM. In this data model, the data is organized in a hierarchical tree-like structure. In such a structure, each record in DBMS is represented as a node.where a parent node organizes and connects to its child nodes, establishing a clear parent-to-child hierarchy. A parent record can have multiple child records, but each child record has only one parent record,
This data model can be easily visualized because each record in DBMS has one parent and many children (possibly 0) as shown in the image given below.

The above-given image represents the data model of the Vehicle database, where vehicles are classified into two types Viz. two-wheelers and four-wheelers and then they are further classified.
The main drawback we can see here is we can only have one too many relationships under this model, hence the hierarchical data model is very rarely used nowadays.
Network Model
A network data model is a flexible way to represent complex relationships between data entities. A network model is nothing but a generalization of the hierarchical data model as this data model allows many to many relationships; therefore, in this model, a record can also have more than one parent. This is achieved through multiple parent segments, which enable the network model to support complex, many-to-many relationships between data entities.
The network model in DBMS can be represented as a graph and hence it replaces the hierarchical tree with a graph in which object types are the nodes and relationships are the edges.
For example -

Here you can see all three departments are linked with the director which was not possible in the hierarchical data model.
In the network model, there can be many possible paths to reach a node from the root node (College is the root node in the above case), therefore the data can be accessed efficiently when compared to the hierarchical data model. But, on the other hand, the process of insertion and deletion of data is quite complex.
Entity-Relationship Model (ER Model)
An Entity-Relationship model is a high-level data model that describes the structure of the database in a pictorial form which is known as ER-diagram. In simple words, an ER diagram is used to represent logical structure of the database easily.
ER model develops a conceptual view of the data hence it can be used as a blueprint to implement the database in the future.
Developers can easily understand the system just by looking at ER diagram.
Let's first have a look at the components of an ER diagram.
- Entity - Anything that has an independent existence about which we collect the data. To learn more about Entity in DBMS click here.
They are represented as rectangles in the ER diagram. For example - Car, house, employee.
- Entity Set - A set of the same type of entities is known as an entity set. For example - Set of students studying in a college.
- Attributes - Properties that define entities are called attributes. They are represented by an ellipse shape.
- Relationships - A relationship in DBMS is used to describe the association between entities. They are represented as diamond or rhombus shapes in the ER diagram.

In the above-represented ER diagram, we have two entities that are Employee and Company, and the relationship among them. Also, in the above-represented ER diagram, we can see that both the employee and company have some attributes and the relationship is of "works in" type, which means the employee works in a company.
Relational Model
This is the most widely accepted data model. In this model, the database is represented as a collection of relations in the form of rows and columns of a two-dimensional table. The overall structure and organization of these relations is defined by the database schema, which acts as the structural blueprint specifying how data is organized, related, and constrained within the database. Each row is known as a tuple (a tuple contains all the data for an individual record) while each column represents an attribute.
For example -
| Stu. Id | Name | Branch |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Naman | CSE |
| 102 | Saloni | ECE |
| 103 | Rishabh | IT |
| 104 | Pulkit | ME |
The above table shows a relation "“STUDENT"” with attributes such as Stu. Id, Name, and Branch which consists of 4 records or tuples. In this example, 'Stu. Id' serves as the primary key, uniquely identifying each record in the table and ensuring data integrity.
Check out this article to learn more about the Relational model in DBMS.
Object-Oriented Data model
As suggested by its name, the object-oriented data model is a combination of object-oriented programming and relational data model. In this data model, the data and their relationship are represented in a single structure which is known as an object.
Since data is stored as objects we can easily store audio, video, images, etc in the database which was very difficult and inconvenient to do in the relational model. As shown in the image below two objects are connected with each other through links.

In the above image, we have two objects that are Employee and Department in which all the data is contained in a single unit (object). They are linked with each other as they share a common attribute Department_Id.
Object Relational Data Model
Again as suggested by its name, the object-relational data model is an integration of the object-oriented model and the relational model. Since it inherits properties from both of the models it supports objects, classes, etc like object-oriented models, and tabular structures like the relational model.
For example -
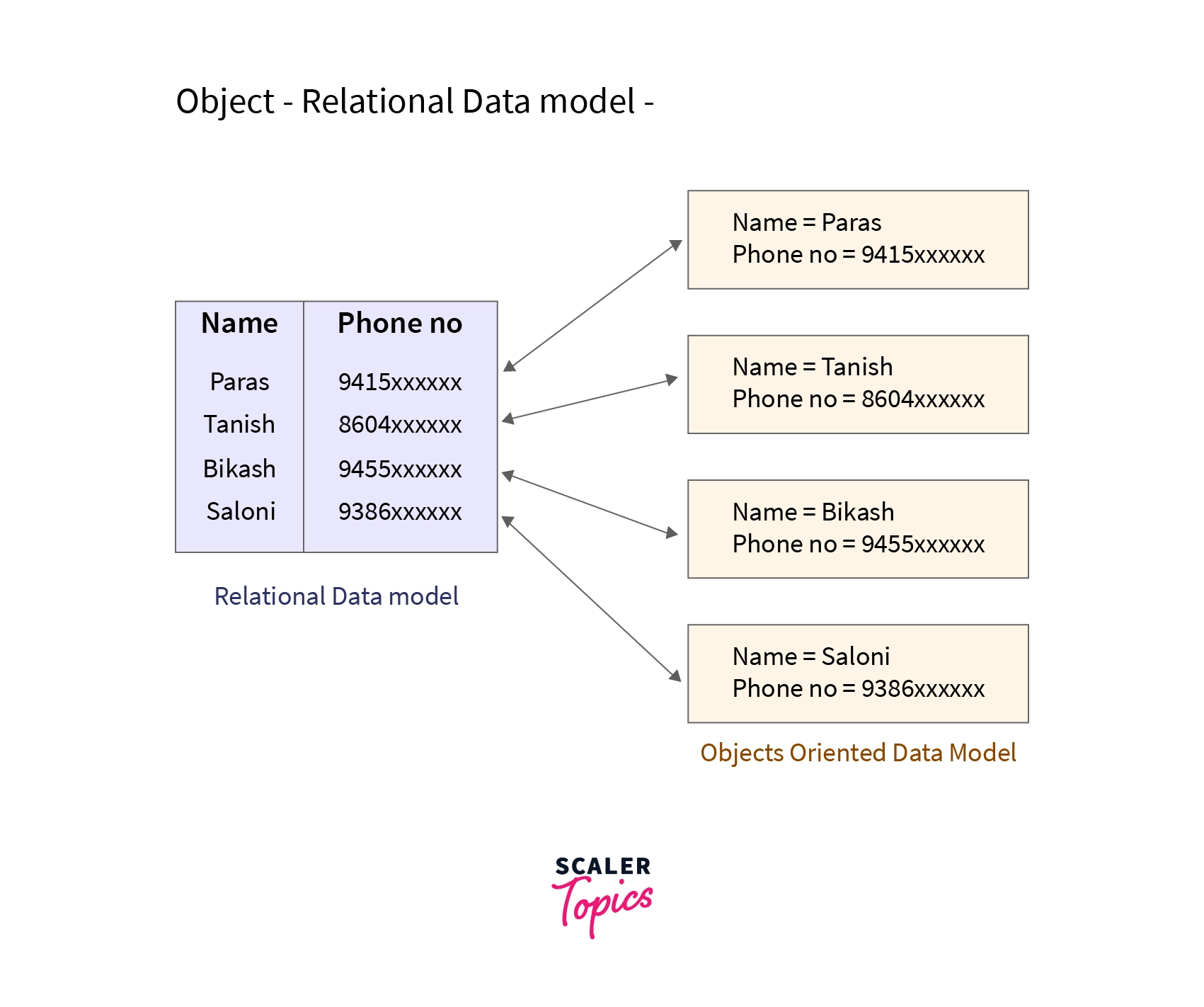
It provides data structures and operations used in the relational model and also provides features of object-oriented models like classes, inheritance, etc. The only drawback of this data model is that it is complex and quite difficult to handle.
Float Data Model
The float data model consists of a single two-dimensional array of data elements. For example, in the 2-d array we can have one column as username and the other as password. One thing that can be noticed here is, there should not be duplicate entries in the table (array).
For example -

The major drawbacks of this model are that it fails to store a huge amount of data secondly, to access any data whole table needs to be searched which makes it inefficient.
Semi-Structured Data Model
A semi-structured data model is a generalized form of the relational model, which allows representing data in a flexible way, hence we can not differentiate between data and schema in this model because, in this model, some entities have a missing attribute(s) and on the other hand, some entities might have some extra attribute(s) which in turn makes it easy to update the schema of the database.
For example - We can say a data model is semi-structured if in some attributes we are storing both atomic values (values that can't be divided further, for example, Roll_No) as well as a collection of values.
Associative Data Model
The associative data model sees the data in the same way as the brain does, entities and relationships between them. The relationship is expressed as a simple English sentence of the form "subject-verb-object".
For example -
From the sentences
- Pulkit is a customer
- Pulkit's customer id is 645.
- Neeraj is a customer
- Neeraj's customer id is 784.
We can make the following table -
| Cust_ID | Name |
|---|---|
| 645 | Pulkit |
| 784 | Neeraj |
Context Data Model
The context model is nothing but a combination of several data models that have been discussed above. For example, a context model can be a combination of a network model, ER model, etc. This data model allows one to do many things which were not possible if he/she use a single data model.
Data Modeling Abstraction Levels
Data modeling abstraction levels are fundamental in designing and managing a database’s logical structure. By breaking down the process into different levels, database designers can focus on specific aspects of the data, making it easier to organize, represent, and implement complex data systems. These abstraction levels help bridge the gap between real-world requirements and the technical implementation within a database model.
Conceptual Level
The conceptual level is the highest abstraction layer in data modeling. At this stage, the focus is on defining what data needs to be stored and how different data entities relate to each other, without worrying about how the data will be physically stored or accessed. This level is typically represented using Entity-Relationship (ER) diagrams, which visually map out entities, their attributes, and the relationships between them. For example, in a relational database model, the conceptual level would outline entities like customers, orders, and products, and show how they are connected. This approach ensures that the database model accurately reflects the business requirements and provides a clear foundation for further design.
Logical Level
Moving down to the logical level, the conceptual design is translated into a logical structure that can be implemented in a database management system. Here, the focus shifts to organizing data into tables, defining columns, specifying data types, and establishing relationships such as primary and foreign keys. The logical level is independent of any specific DBMS but considers how data will be structured for efficient access and management. For instance, in a hierarchical data model, the logical level would define a tree like structure, with parent and child nodes representing the relationships between data elements. This level ensures that the logical structure of the database supports the required data access patterns and maintains data integrity.
Physical Level
The physical level is the most detailed abstraction, dealing with how data is actually stored on disk and accessed by the system. This level involves decisions about data storage formats, indexing, partitioning, and other performance optimizations. In an object oriented data model, for example, the physical level would specify how objects and their relationships are stored in memory or on disk, ensuring efficient data storage and retrieval. The physical level is closely tied to the capabilities of the chosen DBMS and is essential for optimizing performance, scalability, and reliability in large-scale data environments.
Applications of Data Models
-
Data models play a vital role in a wide range of applications across the data industry, from designing robust databases to powering advanced analytics and business intelligence solutions. By providing a structured framework for representing data, data models help organizations manage, access, and analyze their information more effectively.
-
In database design, data models serve as blueprints for creating relational data models, hierarchical models, and other types of data models. A well-structured database model helps ensure data integrity, minimizes data redundancy, and supports efficient data access. For example, a relational database model is commonly used in applications like e-commerce platforms, where entities such as customers, orders, and products need to be organized and related in a logical structure.
-
Data models are also essential in data warehousing, where they define how large volumes of data from different sources are integrated and stored for analysis. Using models like the star schema or snowflake schema, organizations can design data warehouses that support fast and flexible reporting. This enables businesses to analyze trends, monitor performance, and make data-driven decisions.
-
In the realm of business intelligence, data models underpin the creation of dashboards, reports, and visualizations. By organizing data into meaningful structures, such as dimensions and facts, data models make it easier to generate insights and track key metrics. For instance, a company might use an object oriented data model to store and analyze multimedia data, or a relational data model to track sales performance across different regions and time periods.
-
Overall, data models provide the foundation for managing all types of data, from structured to semi structured data models. They help organizations maintain data integrity, reduce data redundancy, and ensure that stored data can be accessed and analyzed efficiently. By understanding and applying different data models—such as hierarchical, network, relational, object oriented, and associative models—businesses can design databases and data systems that meet their unique needs and support their strategic goals.
Advantages of Data Models in DBMS
- Data models ensure that the data is represented accurately.
- The relationship between the data is well-defined.
- Data Redundancy in DBMS can be minimized and missing data can be identified easily.
- Data models help organizations manage data transfer, transformation, and loading across multiple databases and sources, ensuring analysis-ready datasets.
- Last but not least, the security of the data is not compromised.
Disadvantages of Data Models in DBMS
-
The biggest disadvantage of the data model is, one must know the characteristics of physical data to build a data model.
-
Sometimes in big databases, it is quite difficult to understand the data model also the cost incurred is very high.
- Data models in DBMS are used to represent the database's logical structure, which defines how data is organized, related, and manipulated. The database's logical structure is crucial because it shapes the overall functionality and integrity of the database.
Conclusion
- Data models in DBMS are used to represent the logical structure of the database.
- Several types of data models exist with their own advantages and limitations.
- ER model, Relational model, and Object-oriented model are among the most popular data models in DBMS.
